Figure 3. Combinatorial treatment with LDN-193189 and selumetinib results in increased cell death and decreased proliferation of MPNST cells.
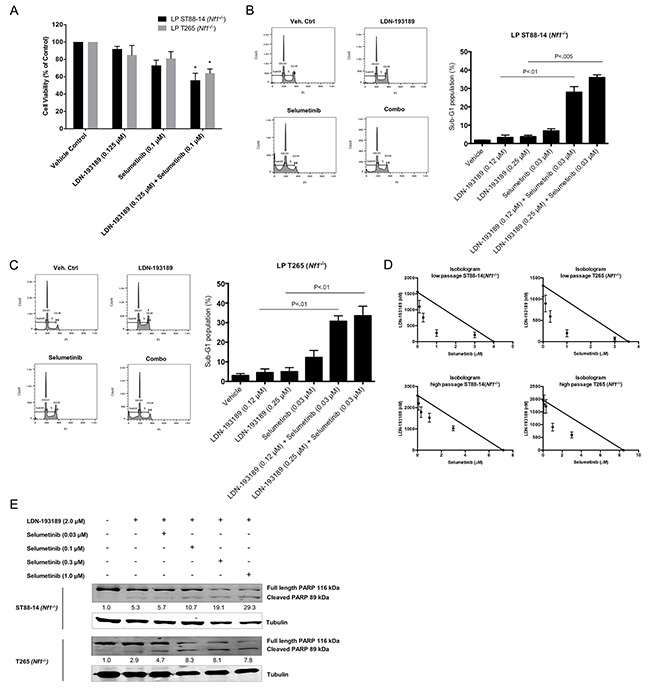
A. Bar graph of the percentage of viable low passage MPNST cells via MTT assay. Cells were treated with the indicated drug concentrations for 48 hours. Single agent treatment with LDN-193189 does not affect cell growth at concentrations below its IC50, however addition of selumetinib significantly decreases the % of viable MPNST cells (n=3, *P<0.05, paired t-test compared to cells treated with LDN-193189 only). B. and C. Representative histograms from cell cycle analyses of low passage NF1-null MPNST cell lines treated with either single agent or combination agents for 48 hours. Bar graph from cell cycle analyses data of MPNST cells treated with biochemically relevant concentrations of LDN-193189 and selumetinib. Percentage of cells in sub-G1 phase increase upon combinatorial treatment with LDN-193189 and selumetinib as compared to single treatment with either of the agents (n=3, paired t-test combination treatment compared to cells treated with LDN-193189 only). D. Standard isobologram analyses of the anti-tumor interactions between LDN-193189 and selumetinib in various MPNST cell lines. All drug combinations exhibit a synergistic effect in low and high passage NF1-null MPNST cells with an increased synergistic interaction in the low passage cells. Each axis represents the indicated concentrations of that drug. Data points represent the average value from three independent experiments ± SD. E. Results from PARP cleavage assay upon 48-hour treatment with candidate drugs indicate a dose-dependent induction of apoptosis upon combination treatment as compared to treatment with LDN-193189 alone. For treatment with LDN-193189 alone, cells were treated with 2.0 μM of LDN-193189 based on the drug's IC50 as determined by the MTT assay. For combination treatment, cells were treated with 2.0 μM of LDN-193189 in combination with biochemically effective increasing concentrations of selumetinib. The relative levels of cleaved PARP were calculated by normalizing their densitometry measurements to tubulin, and then compared to vehicle-treated control (set as 1).
