Figure 7. miR-31 inhibits ARID1A to transactivate pluripotency genes and oncogenicity.
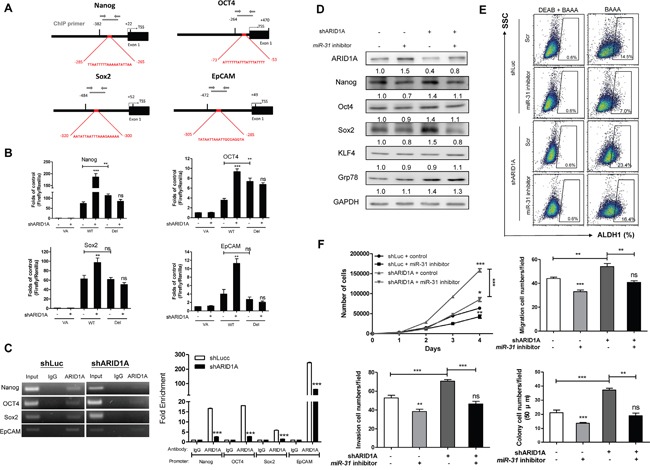
A. Schematic diagrams designate AT-rich sites (Red boxes) in the proximal regions of the Nanog, OCT4, Sox2 and EpCAM promoters. TSS, transcription start site; Thin black bars, the termini of AT-rich sites. Thick black bars define the segments for reporter assay in B. Grey lines define the segments for ChIP assay in C. (B) Promoter activity. Knockdown of ARID1A increases the activity of the WT promoter reporters of each gene, while it does not alter the activity of the Del promoter reporters. Deletion of the AT-rich sites increases the promoter reporter activity of Nanog and OCT4, but it does not alter the promoter reporter activity of Sox2 and EpCAM. (C) Lt, ChIP assays of ARID1A in Nanog/OCT4/Sox2/EpCAM promoter regions. Knockdown of ARID1A reduces the PCR products amplified from the DNA fragments that had been immunoprecipitated by anti-ARID1A antibody. Rt, ChIP qPCR analysis. Input, 2% of total lysate. D-F. Rescue of oncogenicity and stemness in the OECM1 shARID1A 9091 cell subclone and control. (D) Upregulation of Nanog, OCT4 and Sox2, induced by ARID1A knockdown, is reversed by miR-31 inhibition. This does not occur with KLF4 or Grp78. (E) An increase in the ALDH1+ cell population induced by ARID1A knockdown is also reversed by miR-31 inhibition. (F) The proliferation (Upper Lt), migration (Upper Rt), invasion (Lower Lt) and AIG (Lower Rt) are induced by ARID1A knockdown and this is rescued by miR-31 inhibition. Numbers below the Western blot pictures are the normalized values.
