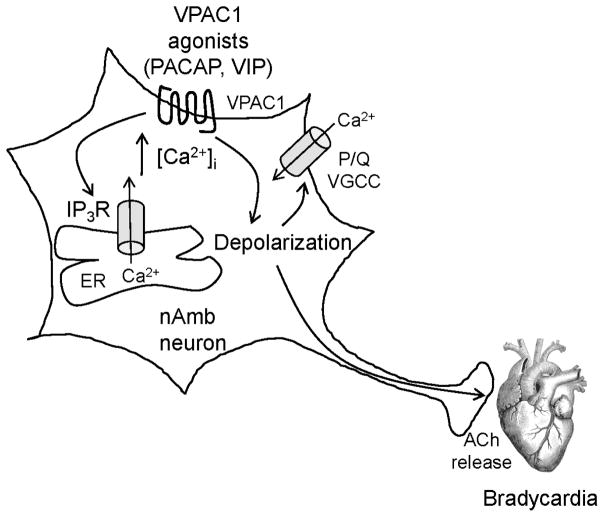
Figure 7. Diagram summarizing the effects of VPAC1 receptor activation in the nucleus ambiguus neurons.
VPAC1 agonists such as PACAP or VIP activate VPAC1 receptor and release Ca2+ from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R). VPAC1 agonists also produce membrane depolarization, facilitating activation of P/Q-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCC) and subsequent Ca2+ influx. The depolarization is transmitted along the axon and leads to the release of acetylcholine (ACh) in cardiac ganglia followed by bradycardia.