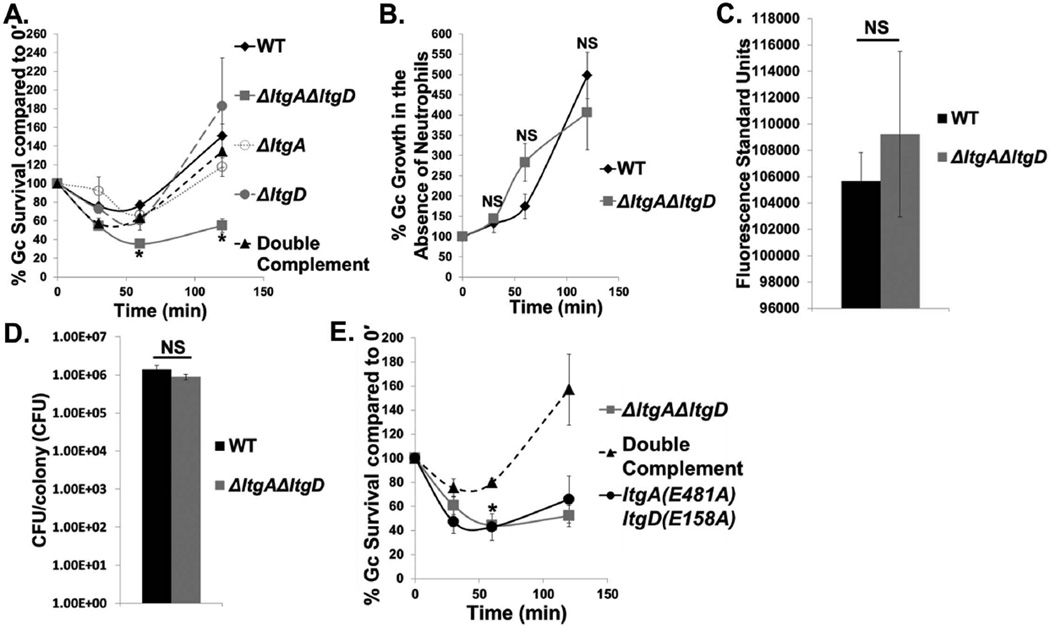
Figure 1. LtgA and LtgD lytic transglycosylase activity is important for Gc survival from primary human neutrophils.
A. WT, ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant, ΔltgA single mutant, ΔltgD single mutant, and ltgA+ ltgD+ double complement Gc were exposed to adherent, IL-8-treated primary human neutrophils. Percent Gc survival was calculated by enumerating CFU from neutrophil lysates at 30, 60, and 120 min divided by CFU at 0 min. *P<0.05 for ΔltgAΔltgD compared to WT, ΔltgA, ΔltgD, and double complement; two-tailed t-test, n = 3 to 14 independent experiments.
B. WT and ΔltgAΔltgD Gc used in Fig. 1A were grown in media in the absence of neutrophils. Percent Gc growth was calculated by enumerating CFU at 30, 60, and 120 min divided by CFU at 0 min. n = 11 independent experiments.
C. WT and ΔltgAΔltgD Gc were diluted to equivalent optical densities and incubated with alamarBlue for 1 hr at 37°C with 5% CO2. n = 3 biological replicates.
D. WT and ΔltgAΔltgD Gc were grown on solid medium for 20 hr. Five colonies each were absorbed on filter paper and suspended in medium. CFU were enumerated after 24 hr incubation and CFU/colony calculated. n = 6 biological replicates.
E. ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant, ltgA+ ltgD+ double complement, and ltgA(E481A)ltgD(E158A) double point mutant Gc were exposed to neutrophils as in Fig. 1A. *P<0.05 for ltgA(E481A)ltgD(E158A) compared to double complement; two-tailed t-test, n = 3 independent experiments.