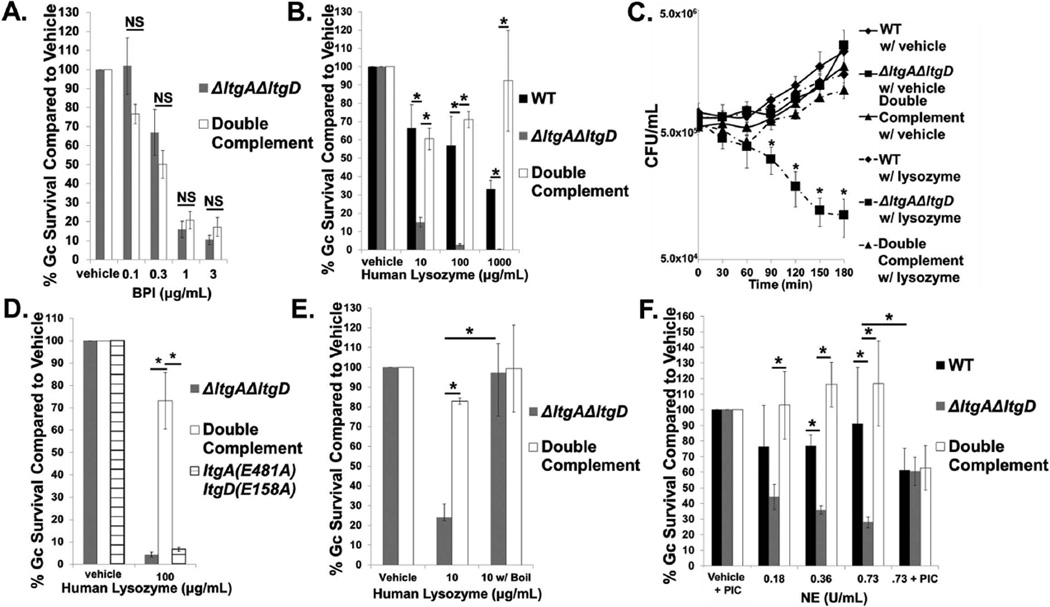
Figure 3. LtgA and LtgD are important for survival from the neutrophil antimicrobials lysozyme and neutrophil elastase.
A. ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant and ltgA+ltgD+ double complement Gc were exposed to increasing concentrations of bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (BPI) or vehicle control for 45 min. Gc survival at each concentration was determined by first dividing CFU/mL at 45 min by CFU/mL at 0 hr and is expressed in relation to survival of vehicle control. n = 4 to 7 biological replicates.
B. WT, ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant, and ltgA+ltgD+ double complement Gc were exposed to increasing concentrations of human lysozyme or vehicle control for 3 hr. Gc survival is expressed as in Fig. 3A. n = 3 to 6 biological replicates.
C. CFU/mL was enumerated for WT, ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant, and ltgA+ltgD+ double complement Gc exposed to 100 µg/mL of human lysozyme or vehicle control. n = 3 biological replicates.
D. ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant, ltgA+ltgD+ double complement, and ltgA(E481A)ltgD(E158A) double point mutant Gc were exposed to 100 µg/mL human lysozyme or vehicle control for 3 hr. Gc survival is expressed as in Fig. 3A. n = 3 biological replicates.
E. ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant and ltgA+ltgD+ double complement Gc were exposed for 3 hr to lysozyme that had been boiled for 1 hr to eliminate PG hydrolase activity. Gc survival is expressed as in Fig. 3A. n = 3 biological replicates.
F. WT, ΔltgAΔltgD double mutant, and ltgA+ltgD+ double complement Gc were exposed to increasing concentrations of neutrophil elastase (NE) or vehicle control for 3 hr. In some experiments, 0.73 U/mL NE and vehicle were incubated with a protease inhibitor cocktail (PIC) for 30 min prior to addition of bacteria and for the duration of bacterial exposure. Gc survival is expressed as in Fig. 3A. n = 3 to 6 biological replicates.
In all cases, *P<0.05; two-tailed t-test.