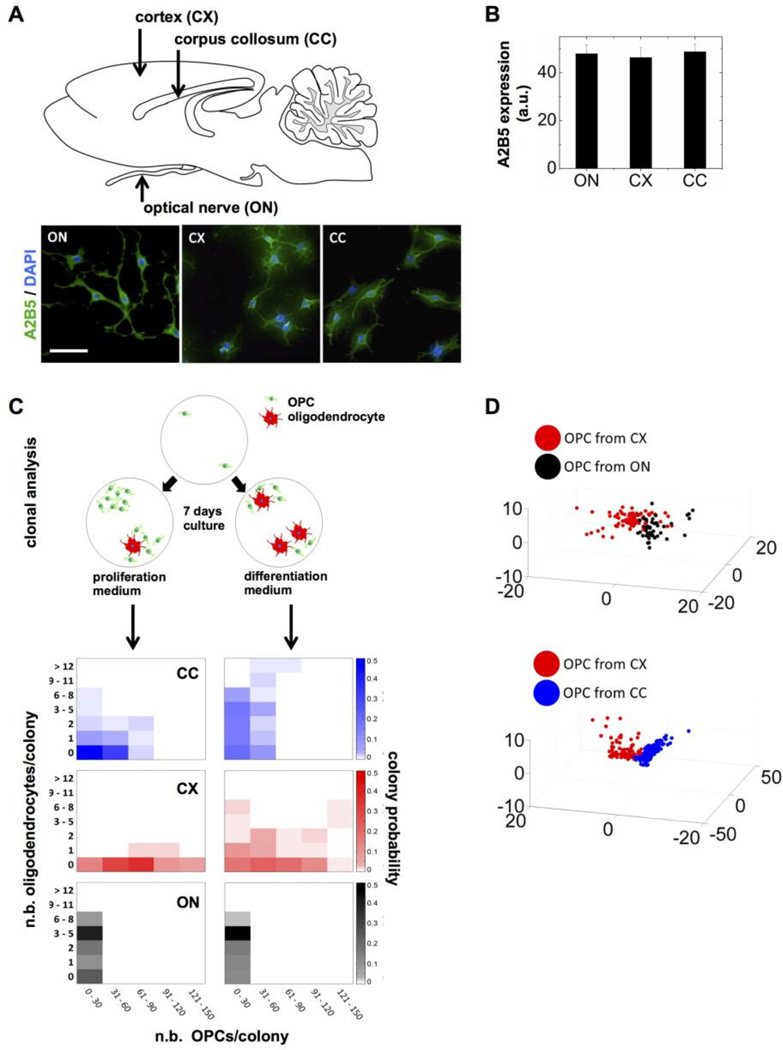
Figure 4. High-content analysis of nuclear descriptors distinguishes OPCs from different brain regions.
(A) Diagram of a sagittal section of the neonatal rat brain highlighting the different regions from which OPCs were isolated. Representative images of freshly isolated OPCs stained with A2B5 antibodies and DAPI are shown; scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Quantification of A2B5 expression based on staining intensity in OPCs isolated from the optic nerve (ON), the cortex (CX), and the corpus collosum (CC). (C) Clonal analysis of OPCs isolated from the ON (black), CX (red) and CC (blue). The OPCs were plated at clonal density and cultured in proliferation and differentiation media for seven days to assess the number and proportion of OPCs (A2B5 positive staining) and of differentiated oligodendrocytes (GalC positive). Each densitogram plot represents 100 clones, where the x, y1, and y2 axes indicate the number of OPCs, oligodendrocytes, and fractional number of clones with a particular composition (indicated by brightness of the corresponding color), respectively. (D) High-content analysis of nuclear descriptors. OPCs were fixed and stained with DAPI and NuMA antibodies 4 hours after isolation. The 3D plots (bottom) represent principal component analyses of nuclear shape combined with NuMA descriptors.