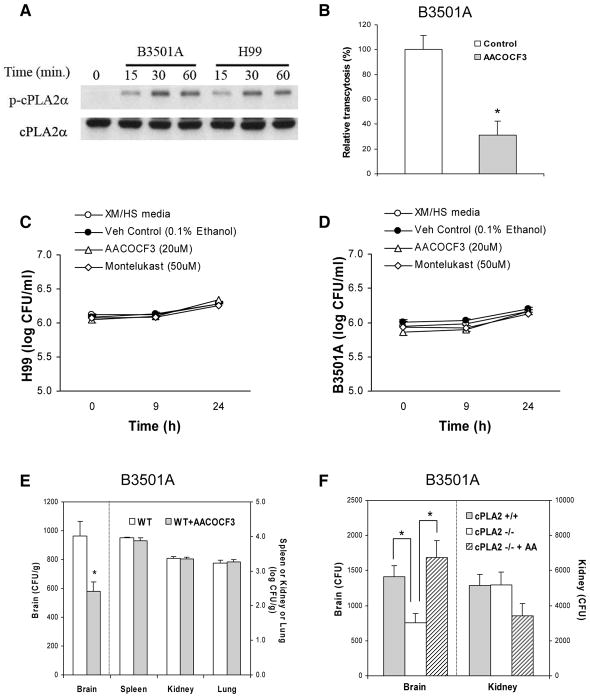
Figure 1. Host cPLA2α is involved in C. neoformans traversal of the HBMEC monolayer and penetration into the brain.
(A) Serine phosphorylation of cPLA2α occurs in response to C. neoformans strains B-3501A and H99 in HBMEC in a time-dependent manner. The lysates of HBMEC incubated with C. neoformans were examined for phospho-cPLA2α and cPLA2α in Western blot analysis using specific antibodies.
(B) AACOCF3 significantly inhibited penetration of C. neoformans strain B-3501A across the HBMEC monolayer. Penetration of B-3501A across the HBMEC monolayer was examined in Transwell filters (8 μm pore size). HBMECs were pretreated with 20 μM AACOCF3 for 60 min and then 20 μM AACOCF3 solution were added to every 2 hr (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hr, respectively) after addition of 1×106 CFU of strain B-3501A to the upper chamber. Our previous studies revealed that traversal of C. neoformans across the HBMEC monolayer was evident over a 9 hr incubation period (Chang et al., 2004). At 9 hr of incubation at 37 °C, sample was taken from the lower chamber and plated for determinations of CFUs. Colonies were counted after 2 days of incubation at 30° C. Transcytosis frequency (%) was determined by (total CFUs recovered from the lower chamber/total number of cryptococcal cells added to the upper chamber) × 100, and expressed as relative frequency compared to transcytosis frequency with vehicle control (0.125% ethanol). Transcytosis frequency of C. neoformans strain B-3501A across HBMEC monolayer at 9 hr of incubation at 37 °C ranged between 1.4 and 8.9 %. Data shown are means ± SEM of triplicates. * P<0.05, unpaired t-test, compared to vehicle control.
(C and D) AACOCF3, a cPLA2α inhibitor, and Montelukast, a CysLT1 receptor antagonist, show no significant effects on growth of C. neoformans strains H99 (C) or B3501A (D).
C. neoformans strains H99 (C) or B3501A (D) were growing in Hams-F12/M199 (1: 1, v/v), 5 % heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (experimental medium, XM) and 5 % fresh human serum (HS) at 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator. Cryptococcus counts were performed at 0, 9, and 24h incubation time. Data shown are mean ± SEM. Each experiment was performed in triplicate.
(E) AACOCF3 decreases C. neoformans B-3501A penetration into the brain of BALB/c mice (WT). 4 mM AACOCF3 in 50μl PBS was injected through tail vein 30 min before, 3 hr and 6 hr after tail vein injection of C. neoformans B-3501A (1×105 cells in 100μl PBS). Control mice were injected with 7% ethanol in100 μl PBS. Cryptococcus counts were determined 24 hr after injection of B-3501A. Data shown are mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, Student’s t-test between WT (n=5), and WT + AACOCF3 (n=5).
(F) C. neoformans penetration into the brain of cPLA2α−/− and their wild type mice. Cryptococcus counts were determined 24 hr after injection of B-3501A (1×105 cells) in 100 μl PBS through tail vein. 40 μM arachidonic acid (AA) in 100 μl PBS (1.2 μg/mouse) was injected through tail vein 30 min before C. neoformans injection. Data shown are mean ± SEM. * P<0.05, Student’s t-test between cPLA2α +/+ (n=5), cPLA2α−/− (n=5), and cPLA2α −/− + AA (n=3).