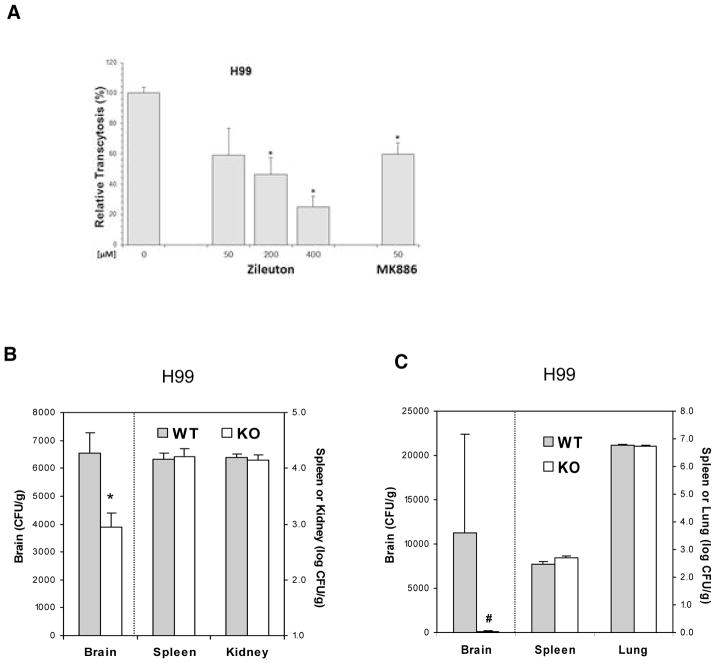
Figure 2. 5-LO is involved in C. neoformans traversal across the HBMEC monolayer and penetration into the brain.
(A) Zileuton (5-LO inhibitor) and MK886 (FLAP inhibitor) inhibited C. neoformans strain H99 traversal of the HBMEC monolayer in a dose-dependent manner. Data shown are means ± SEM of triplicates. * P<0.05, unpaired t-test, compared to vehicle control.
(B) C. neoformans penetration into the brain following intravenous inoculation is significantly decreased in 5-LO−/− mice compared to their wild type animals. The yeast counts from the brain, kidney, and spleen were determined 24 hr after injection of H99 (1×105 cells) in 100μl PBS through tail vein. Data shown are mean ± SEM. * P<0.05 by Student’s t-test between wild type (WT, n=4) and 5-LO−/− mice (KO, n=4).
(C) C. neoformans penetration into the brain following intratracheal inoculation is significantly decreased in 5-LO−/− mice compared to wild type mice. The yeast counts from the brain, spleen, and lung were determined 7d after intratracheal inoculation of H99 (1×105 cells). Data shown are mean ± SEM. # P<0.05 by Wilcoxon Rank Sum test between wild type (WT, n=6) and 5-LO−/− mice (KO, n=6).