Figure 2. Adjusted cerebral vasoreactivity by type of antiretroviral therapy (ART)a.
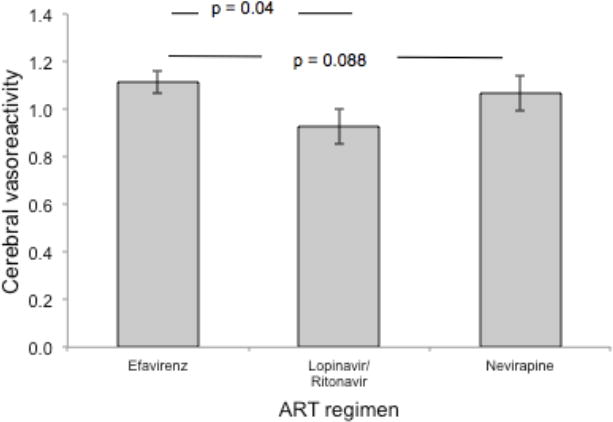
Use of lopinavir/ritonavir was associated with lower mean cerebral vasoreactivity (measured with breath holding index) compared with use of efavirenz, independent of the duration of HIV infection or use of antiretroviral therapy.
aAdjusted for age, statin use, coronary heart disease/myocardial infarction, duration of HIV infection and duration of antiretroviral therapy use.
