Figure 2.
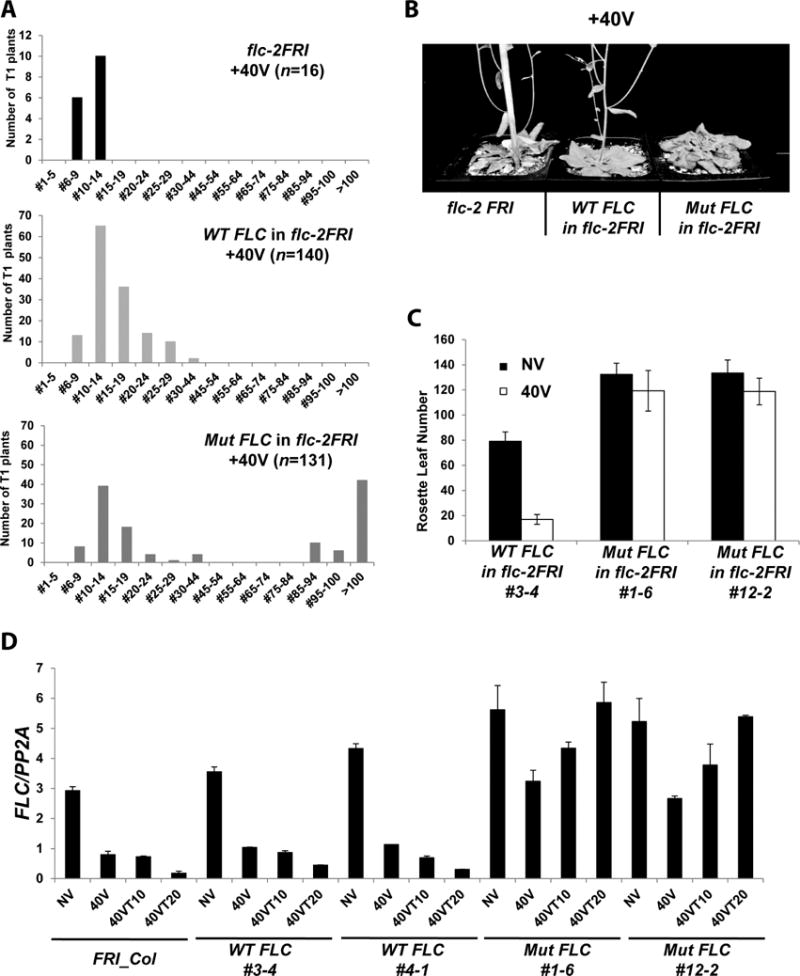
COLDWRAP is necessary for vernalization response. (A) Flowering times of flc-2FRI (parental; top), the primary transgenic lines carrying the wild-type FLC transgene in flc-2FRI after vernalization (middle) and the primary transgenic lines carrying the mutant COLDWRAP in flc-2FRI after vernalization (bottom). X-axis; range of rosette leaf numbers. (B) Representative flowering behaviors of flc-2 FRI, flc-2 FRI transformed with the wild-type FLC transgene, and flc-2 FRI transformed with the mutant COLDWRAP after 40 days of vernalization. (C) Flowering times of a representative transgenic line carrying the wild-type FLC transgene, and two representative lines carrying the mutant COLDWRAP. (D) Changes in FLC mRNA during the course of vernalization in the wild type (FRI_Col) and two representative transgenic lines carrying the wild-type FLC transgene (WT FLC #3-4 and #4-1) and two representative transgenic lines carrying the mutant COLDWRAP (Mut FLC #1-6 and #12-2). Data (relative levels; mean ± SD of quantitative RT-PCR; biological replicates n = 3). Also see Supplementary Figures S3 and S4.
