Figure 2.
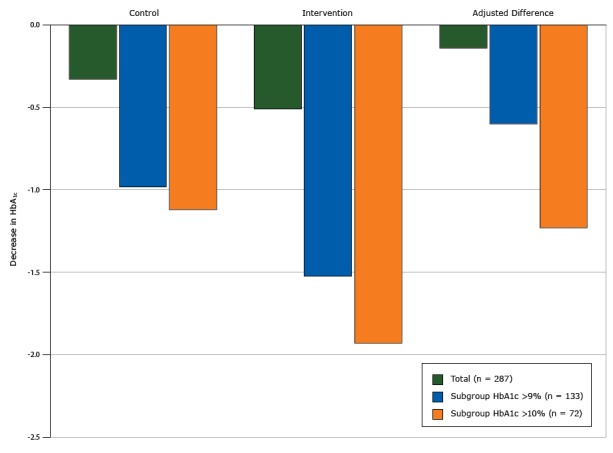
Decreases in glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) from baseline to 12 months by intervention arm, total study population, subgroup with HbA1c higher than 9%, and subgroup with HbA1c higher than 10%, Peer Support for Achieving Independence in Diabetes (Peer-AID) trial using community health workers to provide self-management support among low-income adults with diabetes, Seattle, Washington, 2010–2014. P = .046 for the adjusted difference in HbA1c value between the control and intervention groups for the subgroup with HbA1c higher than 10%.
| Population | Decrease in HbA1c
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Intervention | Adjusted Difference | |
| Total (n = 287) | −0.33 | −0.51 | −0.14 |
| Subgroup HbA1c >9% (n = 133) | −0.98 | −1.52 | −0.60 |
| Subgroup HbA1c >10% (n = 72) | −1.12 | −1.93 | −1.23 |
