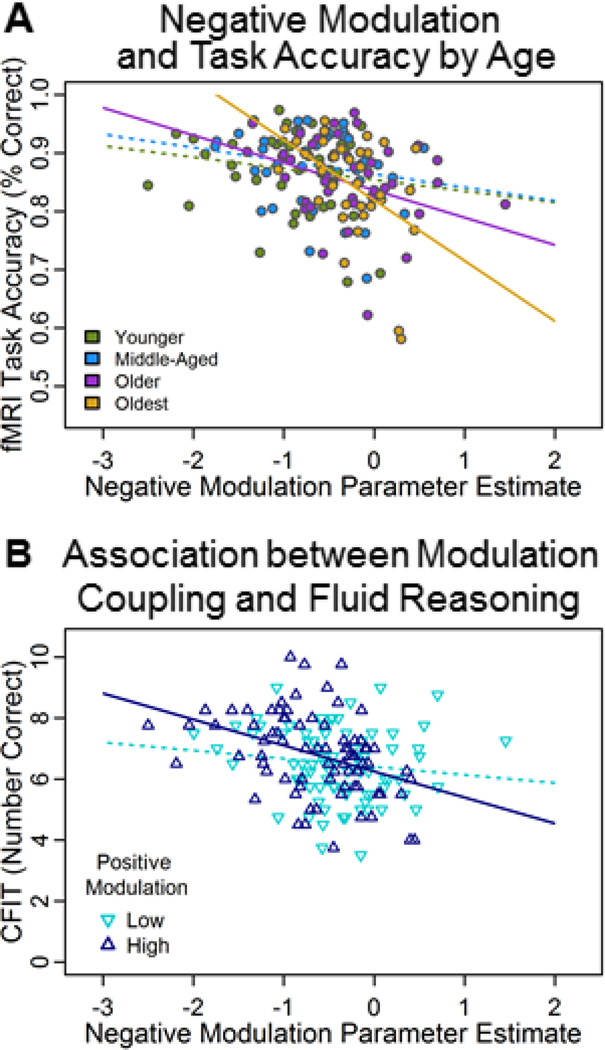
Figure 7. Predicting cognitive performance from modulation to difficulty.
A). More negative modulation to difficulty was associated with greater mean judgment accuracy selectively in old adults (ages 55–69 and 70–94). B). Significant positive modulation by negative modulation interaction indicated an interdependency of these networks, such that those participants showing both high positive modulation in right fronto-parietal regions and greater negative modulation in deactivated regions exhibited higher fluid reasoning (CFIT) scores, regardless of age. Significant regression lines (p ≤ .05) are indicated by a solid line trend; nonsignificant regression lines are indicated by dotted lines.