Figure 2.
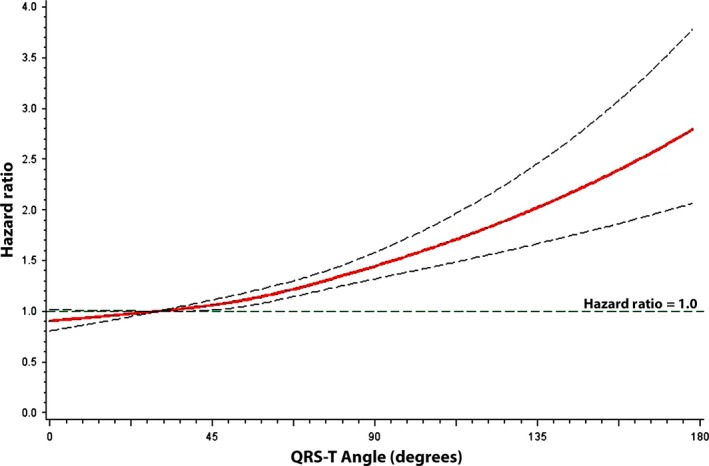
Risk of atrial fibrillation across QRS‐T angle values. Each hazard ratio was computed with the median QRS‐T angle value of 30° as the reference and was adjusted for age, sex, race, education, income, smoking, heart rate, systolic blood pressure, diabetes, body mass index, total cholesterol, high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol, aspirin, antihypertensive medications, coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
