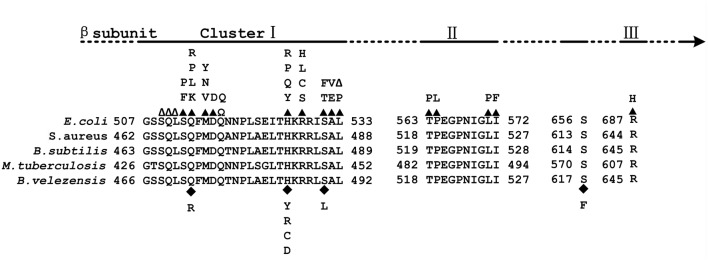
FIGURE 1.
Map of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase β (RpoB) subunit. (Top) Location of Rif clusters I, II, and III. (Bottom) Amino acid sequence alignment of the Rif clusters in E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Bacillus velezensis. The numbering begins at the first amino acid of the RpoB sequences. Well-characterized RpoB substitutions that cause rifampicin resistance in E. coli are noted above the E. coli RpoB sequence. Closed triangles above the E. coli sequence indicate amino acid substitutions; empty triangles indicate amino acid deletions; Ω indicates amino acid insertions; closed diamonds below the B. velezensis sequence indicate amino acid substitutions.