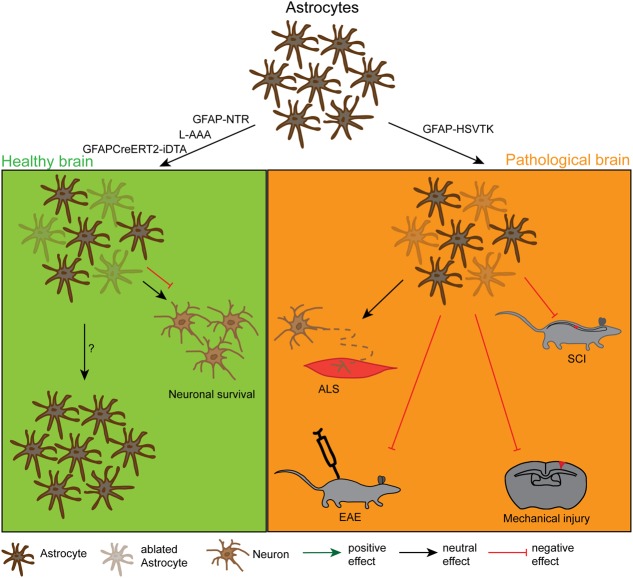
FIGURE 2.
Effects and dynamics of astrocyte ablation under healthy and pathological conditions. Under physiological conditions (left green panel) successful astrocyte ablation has been achieved by the use of the pharmacological drug L-α-aminoadipic acid (L-AAA) or the GFAPCreERT2-DTA and the GFAP-NTR mouse lines. For the astrocytes, the repopulation kinetics have not been analysed in detail yet, but these cells were also shown to repopulate the depleted area. As a functional outcome, the ablation did either not show an effect or had a negative effect on neuronal survival in the cerebellum and the spinal cord. Under pathological conditions (right orange panel) astrocyte ablation was solely achieved by the use of the GFAP-HSVTK mouse line. However, with this model only the pool of proliferating astrocytes can be depleted. The reduction of scar forming astrocytes in general had a negative outcome for the injury size and severity in spinal cord injury (SCI), mechanical brain injury and EAE. It did not affect the pathology in a model of ALS, but this could be due to the low amount of proliferating astrocytes in this model.