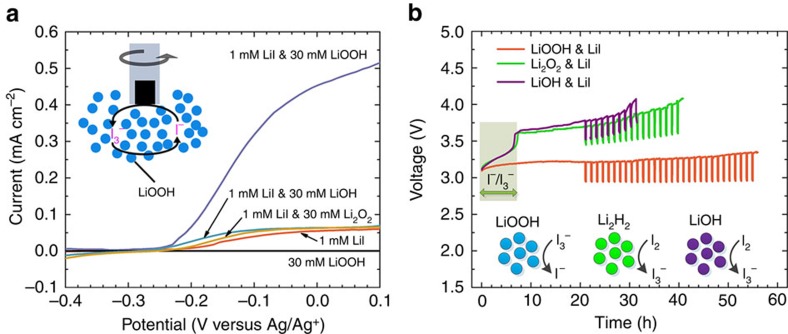
Figure 3. Electrochemical properties of LiOOH and the comparisons with LiOH and Li2O2.
(a) RDE measurements of 1 mM LiI in 0.1 M LiTFSI/DME with 30 mM LiOOH·H2O, Li2O2 or LiOH dispersed in the solution. For comparison, the same measurements were conducted in the absence of LiI or lithium compounds suspension in the electrolyte. The rotating rate was 1,200 r.p.m. and the scan rate was 0.01 V s−1. The inset illustrates the catalytic reaction between LiOOH and I3− upon RDE measurement. (b) The charging curves of Li-LiOOH, Li-Li2O2 and Li-LiOH cells. Lithium foil was used as anode. LiOOH·H2O precipitate, Li2O2 or LiOH powder in great excess to LiI in catholyte was loaded onto the cathode before the cells were assembled. The catholyte was 1 ml 0.5 M LiTFSI/DME containing 40 mM LiI. A LAGP membrane was used to segregate the two cell compartments. The cells were first charged at a constant current of 0.1 mA cm−2 for 21 h, and then followed by GITT measurement (2 h charging at the same current plus 10 min resting).