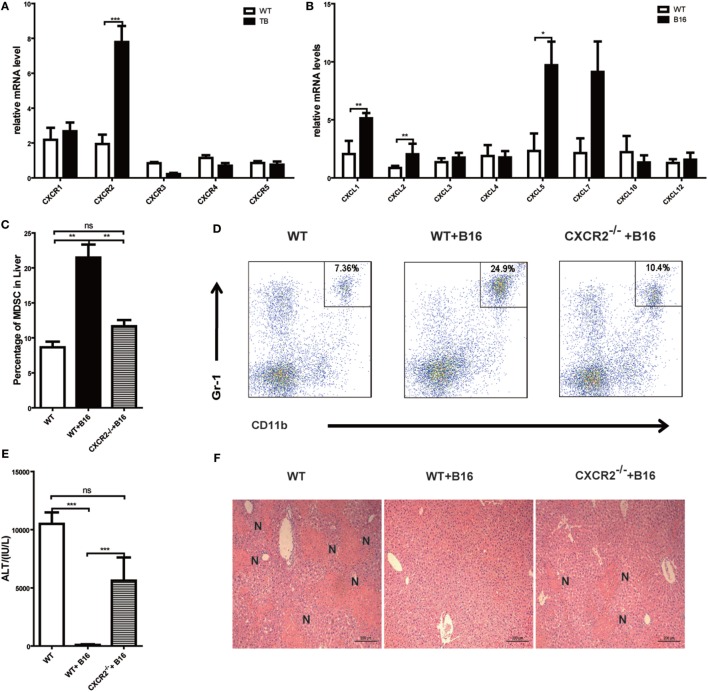
Figure 6.
Recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) into tumor-bearing (TB) (B16) mice livers was CXCR2 mediated. (A) Liver mononuclear cells (MNCs) were isolated from either wild-type (WT) or TB mice 15 days posttumor inoculation, and mRNA levels of CXCRs were determined via quantitative real-time PCR (n = 3). (B) Liver tissues were isolated from either WT or TB mice 15 days posttumor inoculation, and mRNA levels of CXCRs were determined via quantitative real-time PCR (n = 3). (C) CXCR2-dependent liver recruitment of MDSC in TB mice. Sex- and age-matched WT mice and CXCR2−/− mice were either untreated or inoculated with B16 tumor cells to prepare TB mice as described above, and liver MNCs was prepared from the livers and then used for analyzing the percentage of CD11b+Gr1+ through flow cytometry (n = 6). (D) One representative FACS plot in panel (C) is shown. (E) Deficiency of CXCR2 rendered susceptibility to Con A-induced liver damage in TB mice. Sex- and age-matched WT or CXCR2−/− mice were injected with B16 tumor cells, and on day 15 posttumor inoculation, mice were challenged with concanavalin A (Con A). Serum samples collected at 12 h post-Con A injections were used for analyzing the levels of alanine aminotransferase (n = 6). (F) Liver tissues were fixed for hematoxylin and eosin staining, and one representative tissue staining is shown. Scale bars, 200 µm.