Figure 5.
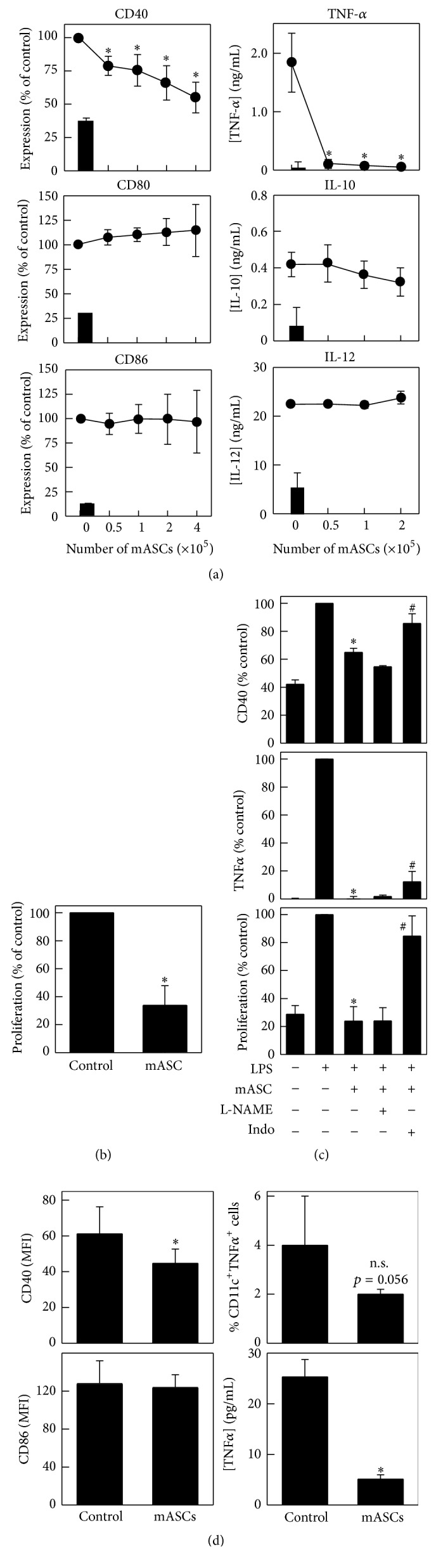
mASCs inhibit the maturation/activation of dendritic cells in vitro and in vivo. (a) mASCs inhibit the maturation of DCs in vitro. Bone marrow-derived DCs from C57BL/6 mice (4 × 105 cells/well) were matured/activated with LPS (1 μg/mL) in the absence or presence of different numbers of mASCs. After 48 hours, nonadherent or loosely adherent cells were harvested (>95% CD11c+ DCs) and analyzed for surface expression of CD40, CD80, and CD86, and the culture supernatants were analyzed for TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-12 content by ELISA. Data for nonstimulated immature DCs are shown as black bars. Results are shown as mean (SEM) of 3 (CD40, CD80, and CD86 FACS and IL-12 ELISA) or 4 (IL-10 and TNF-α ELISA) independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05 versus control (no mASCs). (b) mASC-treated DCs show impaired costimulatory activity on T cells. C57Bl/6 DCs (4 × 105 cells) were LPS-matured in the absence (control) or presence of mASCs (2 × 105 cells) for 48 hours and then added to allogeneic BALB/c splenocytes (used as responders). The proliferation in the MLR was measured by [3H]-thymidine incorporation. Results are shown as mean (SEM) of 3 independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05 versus control. (c) COX-1/2 but not iNOS activity is partly responsible for the effect of mASCs on DC maturation. C57Bl/6 DCs (4 × 105 cells) were LPS-matured in the absence or presence of mASCs (2 × 105 cells) and L-NAME (1 mM) or indomethacin (20 μM) for 48 hours. Expression of CD40 was determined in CD11c+ cells by flow cytometry (5 independent experiments) and the levels of TNF-α in culture supernatants were measured by ELISA (3 independent experiments). The costimulatory activity of the mASC-treated DCs was determined in a MLR using BALB/c splenocytes as responders (4 independent experiments). Results are expressed as percentage of values found with control samples treated with LPS alone in the absence of mASCs and shown as mean (SEM) of the independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus mASCs. (d) mASC treatment impairs DC function in DLNs of EAE mice. C57BL/6 mice with initial EAE symptoms (scores 1-2) were injected intraperitoneally with allogeneic mASCs (106 cells/mouse) isolated from BALB/c mice. After 7 days, DLN cells from untreated (mean score 4.6 (1.0)) and mASC-treated mice (mean score 2.1 (1.0)) were analyzed for the expression of surface CD11c, CD40 (n = 8 mice/group), and CD86 (n = 5 mice/group) and intracellular TNF-α (n = 4 mice/group) by flow cytometry as described in Materials and Methods. CD11c+ DCs were purified by magnetic separation from DLNs from untreated (control) or mASC-treated mice (n = 4 mice/group), restimulated (2.5 × 105 cells/mL) with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 24 hours, and the TNF-α levels in supernatants are determined by ELISA (lower right panel). Results are shown as mean (SD). ∗p < 0.05.
