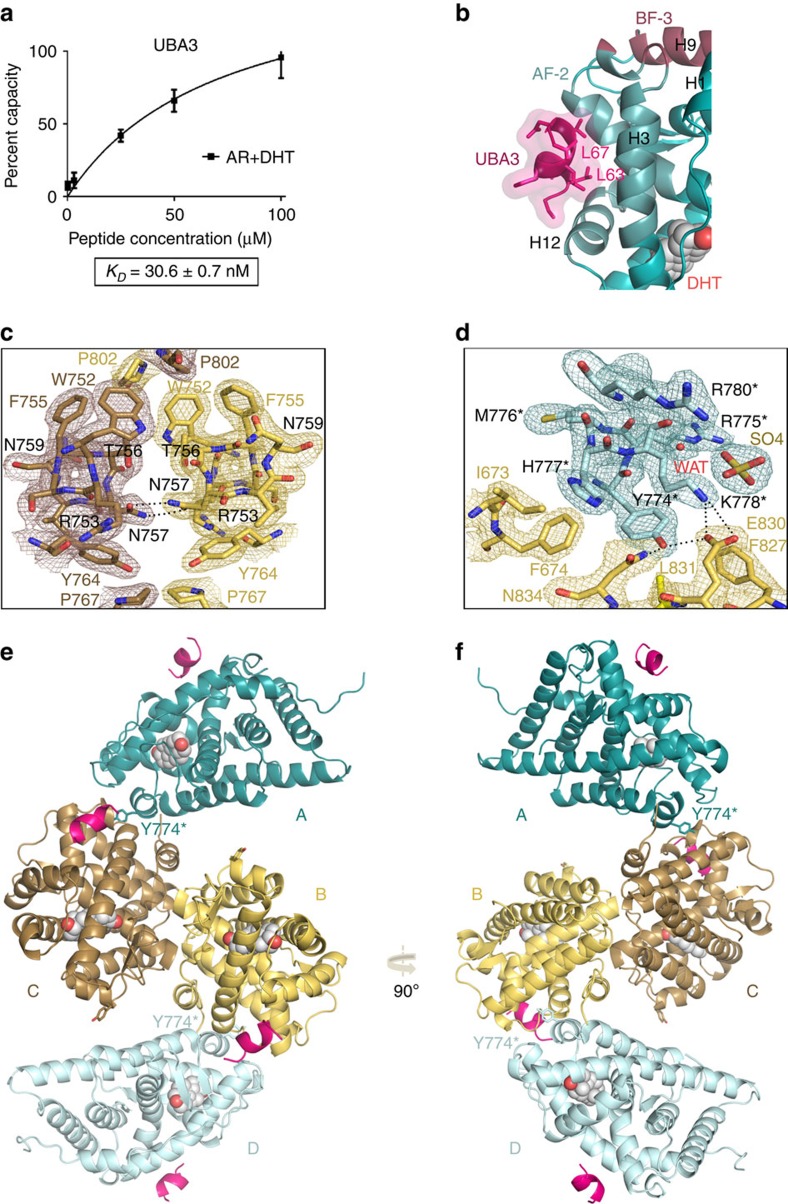
Figure 1. Crystal structure of AR-LBD in complex with UBA3 peptide.
(a) An UBA3 peptide comprising the canonical LxxLL motif binds tightly to AR-LBD. The results of SPR studies conducted in triplicate are shown. (b) Closeup around the AF-2 binding groove with the bound UBA3 peptide shown as a cartoon (pink, with leucine side chains represented as sticks). AR is also depicted as a cartoon with AF-2 and BF-3 binding areas highlighted in brighter blue and magenta, respectively, and the bound DHT moiety in sphere representation. (c,d) Details of the final electron density map. Most relevant AR-LBD residues are represented as sticks and H-bonds with black dotted lines. (c) Closeup showing major interactions across the interface of the core dimer composed by the arbitrarily labelled molecules B (in yellow) and C (in brown). Electron density is shown as either a brown or yellow mesh contoured at 1σ. (d) Closeup showing docking of H6 from peripheral AR-LBD molecule A (pale blue) into the BF-3 pocket of AR-LBD molecule B (yellow). Residues from the peripheral monomer are marked with an asterisk. (e,f) Two views of the AR-LBD crystal structure with the four independent AR-LBD molecules (a–d) found in the ASU. Notice that AR-LBD monomers B (yellow) and C (brown) form a symmetrical core dimer, while the two peripheral AR-LBD labeled as (a) shown (teal) and (d) (pale blue) are associated to the BF-3 grooves of (b,c) respectively.