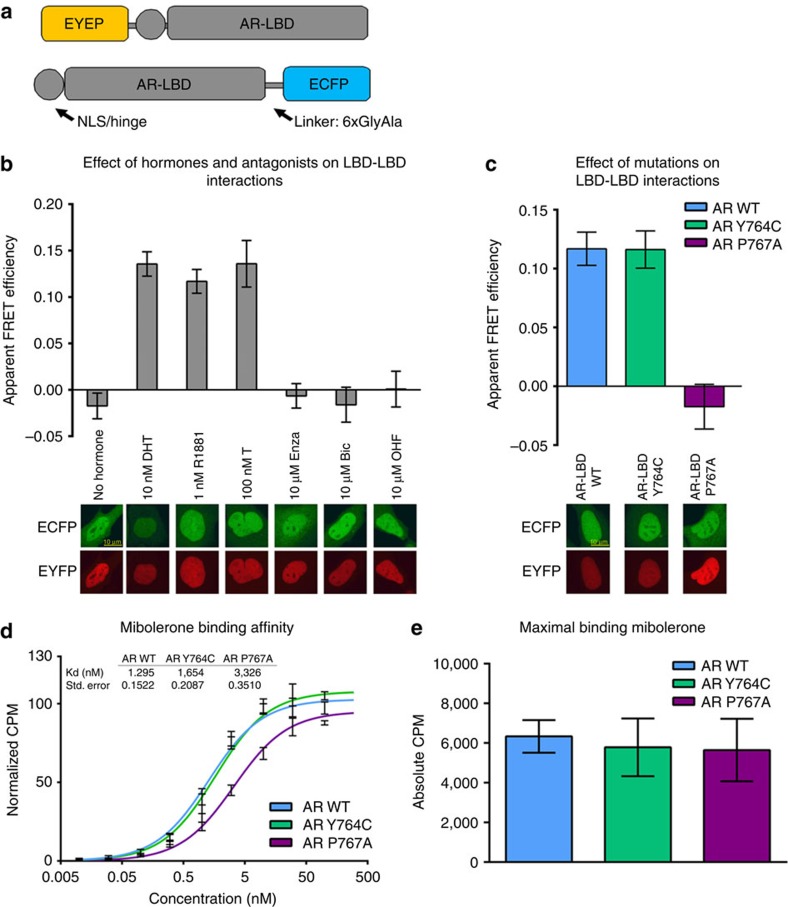
Figure 4. Functional characterization of homotypic AR-LBD interactions by FRET.
(a) Schematic representation of the generated fusion proteins. (b) Acceptor photobleaching FRET of N-terminal and C-terminal fusions of AR-LBD shows agonist-induced interactions (DHT, (n=65), T (n=32), and R1881 (n=48), while no interactions were observed without hormone (n=44) or when antagonists (Bic (n=38), Enza (n=46), and OHF (n=44)) were bound to the LBD (mean values and standard error of the mean of at indicated number of cells are shown). Representative confocal images of cells expressing the fusions of AR with EYFP/ECFP in the presence of these compounds are displayed below the bars. (c) Acceptor photobleaching FRET of indicated proteins shows loss of interaction for the AR P767A mutant (n=67) when compared with the WT (n=59), but not for the Y764C mutant (n=63; mean values and s.e.m. of indicated number of cells are shown). Representative confocal images of Hep3B cells transiently expressing the indicated protein in the presence of DHT are displayed below the bars. (d) Binding affinity of the EYFP-AR-LBD fusion protein for the AR agonist mibolerone. (e) Maximal binding of WT and mutant AR for mibolerone (mean values and standard error of the mean of three experiments with three technical replicates each are shown).