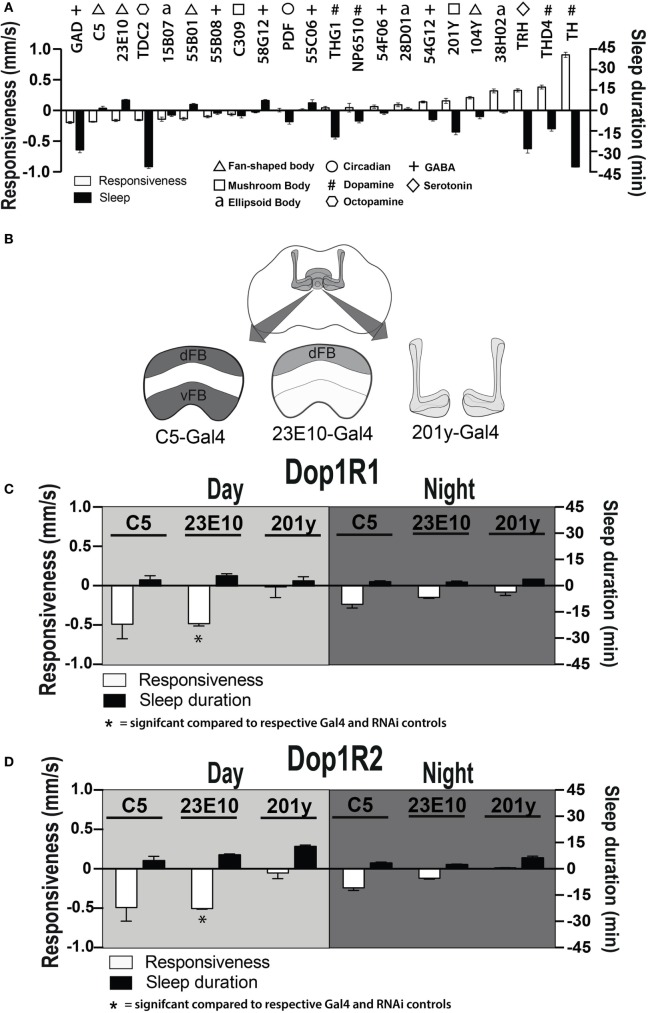
Figure 7.
Manipulating sleep-promoting neurons impairs behavioral responsiveness. (A) 22 Gal4 circuits were activated with UAS-NachBac and resulting adult progeny were behaviorally characterized. Average nighttime responsiveness (white bars, mm/s ± SEM) or sleep duration (black bars, min ± SEM) for each strain is shown relative to the Gal4 genetic control. Different neuronal categories are indicated with symbols. N = 51 for all genotypes, including each respective Gal4 genetic control. (B) Schema of central brain regions associated with C5-Gal4, 23E10-Gal4, and 201y-Gal4 expression. dFB, dorsal fan-shaped body; vFB, ventral fan-shaped body. (C) Average daytime and nighttime responsiveness and sleep duration (±SEM) of treated C5-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R1; tubulin (tub)-Gal80TS animals, 23E10-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R1; tub-Gal80TS animals, and 201y-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R1; tub-Gal80TS animals (N = 56, 81, and 56, respectively), normalized to their corresponding Gal4 control (C5-Gal4/+; N = 108, 23E10-Gal4/+; N = 159, 201y-Gal4/+; N = 41), and compared to both Gal4 and RNAi (UAS-Dop1R1; tub-Gal80TS/+, N = 81, not shown) genetic controls. (D) Average daytime and nighttime responsiveness and sleep duration (±SEM) of treated C5-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS animals, 23E10-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS animals and 201y-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS animals (N = 34, 66, and 30, respectively), normalized to their corresponding Gal4 control (C5-Gal4/+; N = 108, 23E10-Gal4/+; N = 159, 201y-Gal4/+; N = 41) and compared to both Gal4 and RNAi (UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS/+, N = 32, not shown) genetic controls. *P < 0.05, by one-way ANOVA, adjusted for multiple comparisons by a Post Hoc Tukey’s test.