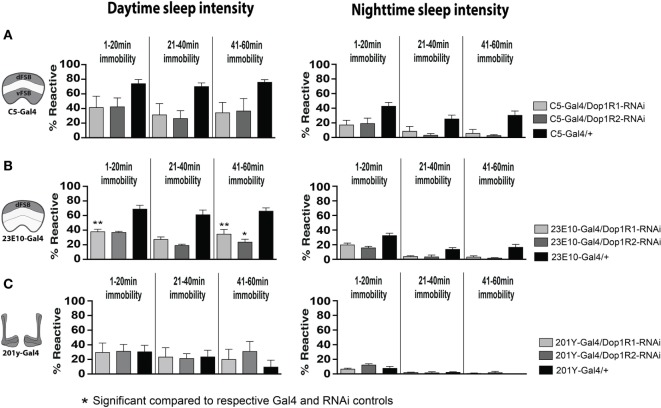
Figure 8.
Transient 23E10-Gal4 driven knockdown of D1 receptors during development increases daytime sleep intensity in adult flies. (A) Daytime (left) and nighttime (right) sleep intensity (% reaction proportion ± SEM) of treated C5-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R1; tubulin (tub)-Gal80TS animals (light gray, N = 56) and C5-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS (dark gray, N = 34) compared to C5-Gal4/+ (black, N = 108) and RNAi (UAS-Dop1R1; tub-Gal80TS/+, N = 81, not shown) genetic controls. (B) % reaction proportion (±SEM) of treated 23E10-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R1; tub-Gal80TS animals (light gray, N = 81), and 23E10-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS (dark gray, N = 66) during the day (left) and night (right) compared to 23E10-Gal4/+ (black, N = 159). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, decreased% reaction proportion compared to both genetic controls, by one-way ANOVA, adjusted for multiple comparisons by a Post Hoc Tukey’s test. (C) % reaction proportion (±SEM) of treated 201y-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R1; tub-Gal80TS animals (white, N = 56) and 201y-Gal4/UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS (dark gray, N = 30) compared to 201y-Gal4/+ (black, N = 41) and RNAi (UAS-Dop1R2; tub-Gal80TS/+, N = 32, not shown) genetic controls.