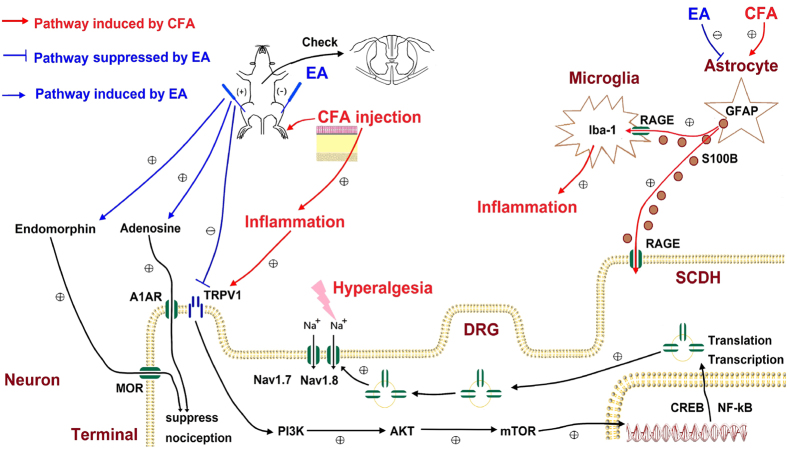
Figure 10. Schematic illustration of neuronal and non-neuronal mechanisms in EA-mediated analgesia of CFA-induced inflammatory pain.
Summary diagram of how astrocyte, glial cells, and TRPV1 is crucial for inflammatory pain and related mechanisms. Our results show that EA can reduce S100B release from non-neuronal cell. We also indicated that EA can trigger the release of opioid and adenosine receptors for relieving inflammatory pain through TRPV1 pathway.