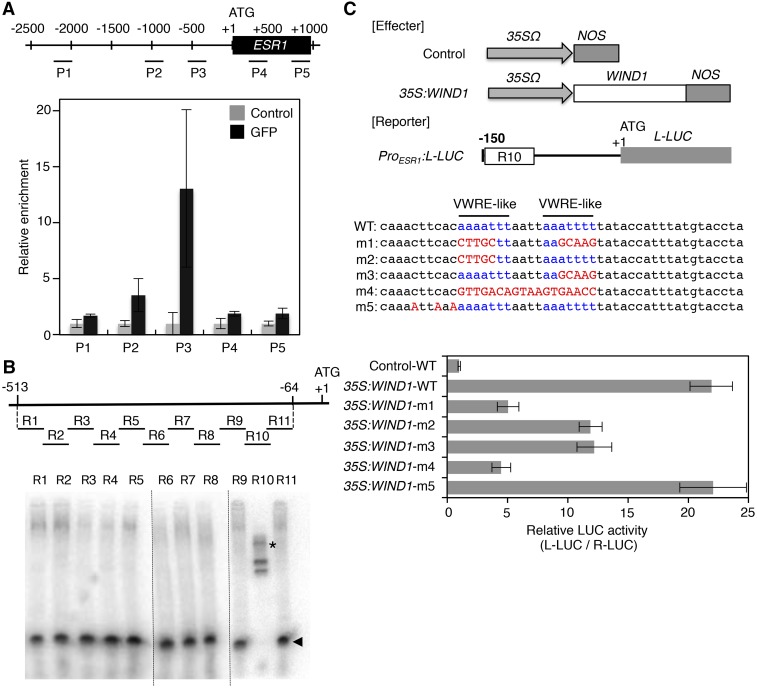
Figure 2.
WIND1 Directly Binds the ESR1 Promoter and Activates Its Expression.
(A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation of WIND1-GFP fusion proteins on the ESR1 locus. Quantitative PCR analysis, using P1-P5 primers designed within the promoter and coding sequence of ESR1, shows the strongest enrichment of WIND1-GFP using P3 primers designed around −500 bp upstream of the translational start site. The black box represents the coding sequence of ESR1 and +1 ATG indicates the translational start site. Black lines mark the relative distance from the translational start site. Data are normalized against input DNA and shown as a relative enrichment of DNA immunoprecipitated with rabbit serum (control). Data are mean ± se (n = 3, technical replicates).
(B) EMSAs of MBP-WIND1-His6 protein’s binding to the ESR1 promoter in vitro. Upper panel shows the position of ∼50-bp DNA probes, designated as R1 to R11, that cover −513 to −64-bp nucleotides of the ESR1 promoter. Arrowheads and asterisks show free and shifted DNA probes, respectively. Dashed lines separate results obtained in three different experiments. Note that the band shifts only with the R10 probe, indicating that MBP-WIND1-His6 binds −153 to −104 bp upstream of the translational start site.
(C) WIND1-induced transient activation of the ESR1 expression in Arabidopsis culture cells. Upper panel shows the effector constructs, control and 35S:WIND1, and the reporter construct, ProESR1:L-LUC. For the effector constructs, gray arrows mark 35SΩ, the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter with the tobacco mosaic virus omega translation amplification sequence, and gray boxes mark NOS, the Agrobacterium tumefaciens nopaline synthase transcriptional terminator. The white box marks the WIND1 coding sequence. For the reporter construct, the black bar represents the 150-bp promoter sequence of ESR1 with the R10 sequence marked with a white box. The gray box represents the coding sequence of L-LUC, encoding a firefly luciferase gene, and +1 ATG indicates the translational start site. The middle panel shows the wild-type R10 sequence with two VWRE-like motifs marked in blue and m1 to m5 mutations marked in red. Bottom panel shows the ESR1 promoter activity as judged by the L-LUC activity relative to R-LUC, Renilla luciferase. Cobombardment of 35S:WIND1 and ProESR1:L-LUC activates the ESR1 promoter. Note that abolishing each of the two VWRE-like motifs by m2 or m3 mutation results in reduced ESR1 induction and abolishing both motifs by m1 or m4 mutation has additive effects, indicating that both motifs are required for activation of ESR1 by WIND1. Data are mean ± se (n = 6, technical replicates).