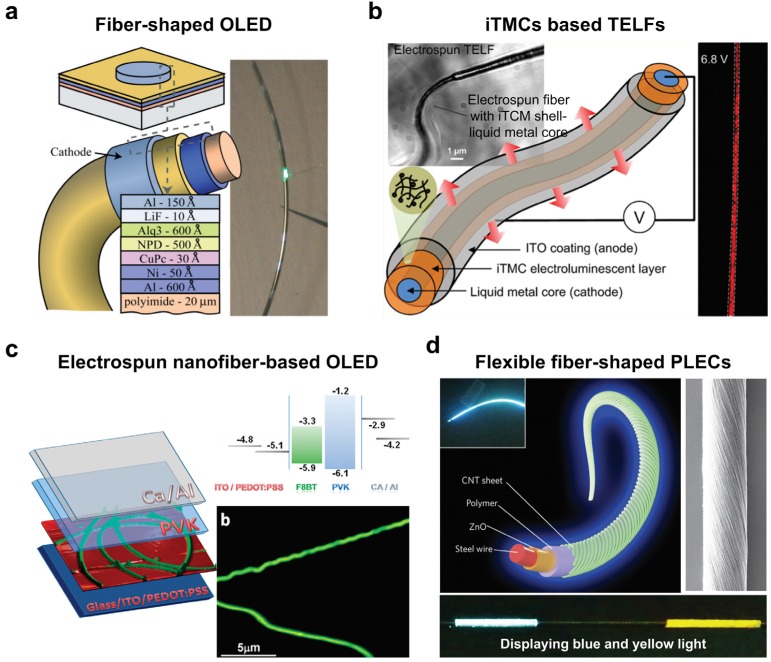
Figure 6.
(a) Schematic illustration of a fiber-shaped organic light emitting diodes (OLED) structure compared with a typical OLED structure and a photograph of a flexed fiber with a green light-emitting pixel; (b) Schematic illustration and optical image of ionic transition-metal complex (iTMCs)-based electro-luminescent nanofibers (TELFs) fabricated via coelectrospinning and luminescence response of TELF under an applied voltage of 6.8 V; (c) Schematic of the conjugated polymer electrospun nanofiber-based OLED structure (left), energy level diagram (right top), and fluorescence microscopy image of an electrospun nanofiber, F8BT-PEO (right bottom); (d) Schematic illustration showing the structure of flexible fiber-shaped polymer light-emitting electrochemical cells (PLECs). Left inset: photograph of a fiber-shaped PLEC biased at 10 V, right inset: aligned CNT sheet wrapped around the modified stainless steel wire, and bottom inset: PLEC displaying blue and yellow light. Reproduced from [42,43,134,135] with permissions by John Wiley & Sons, Copyright 2007 and by ACS Publications, Copyright 2012, 2011 and by Nature Publishing group, Copyright 2015.