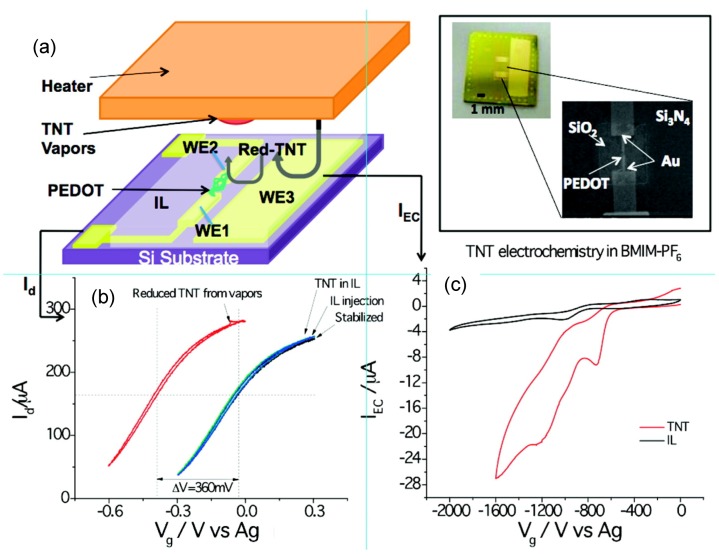
Figure 7.
(a) A hybrid nanosensor consisting of a conducting polymer nanojunction (polymer bridged between WE1 and WE2) and a working electrode (WE3) on a Si chip. The chip is covered with a thin layer of ionic liquid (BMIM-PF6) serving as an electrolyte and preconcentration medium. Upon heating TNT particulates (to 60 °C), TNT vapor is generated which is collected by the ionic liquid layer. The analyte is reduced and detected electrochemically on WE3, and the reduction products are detected by the polymer nanojunctions. Inset: Optical micrograph of the sensor chip used and an SEM image of the PEDOT nanojunction; (b) Current (Id) via the PEDOT nanojunction plotted as a function of WE1 potential before and after exposure to TNT; (c) Cyclic voltammograms of a blank BMIM-PF6 solution (black) and 4 ppm TNT in BMIM-PF6 (red). The large reduction current in the latter case is due to the reduction of TNT. Note that an Ag wire quasi-reference electrode and a Pt counter electrode are used. With permission from [55]; Copyright 2010, American Chemical Society.