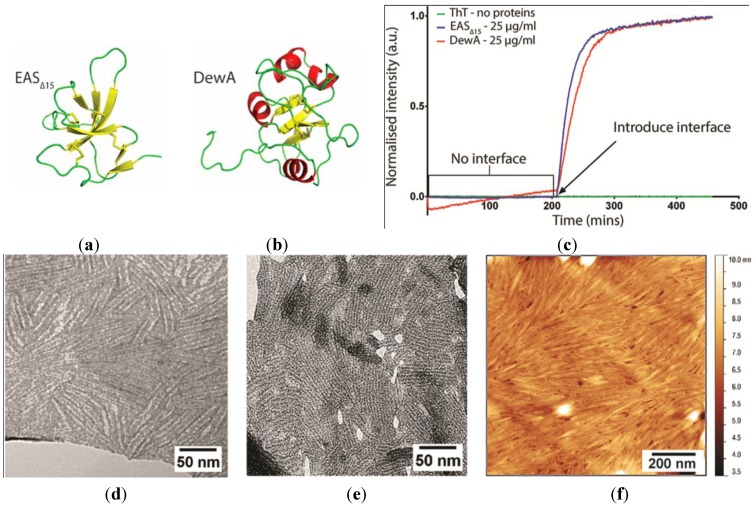
Figure 1.
Solution structures of the soluble forms of Class I hydrophobins: (a) EAS∆15 and (b) DewA, determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Ribbon representations of protein molecular structure were prepared from Protein Data Bank (PDB) entries 2K6A and 2LSH using the molecular graphics program PyMol [24]. (c) Rodlet assembly by EAS∆15 and DewA assayed by Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence demonstrates that these Class I hydrophobins only assemble into amyloid-like rodlets after introduction of a hydrophilic-hydrophobic interface. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of negatively stained: (d) EAS∆15 and (e) DewA hydrophobin rodlet monolayers, transferred from the surface of protein droplets and imaged through the holes in a holey film. (f) Atomic force microscopy (AFM) of the rodlets formed when a 5 µg/mL DewA solution was allowed to dry overnight onto a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) surface.