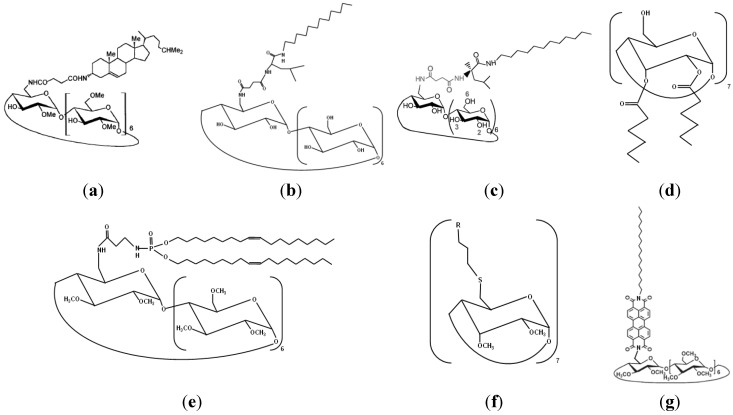
Figure 1.
Amphiphilic cyclodextrins obtained by modifications of the macrocycle: (a) cholesteryl-cyclodextrin; (b) peptidolipidyl-cyclodextrin; (c) monolauryl-cyclodextrin; (d) hexanoyl-cyclodextrin; (e) phospholipidyl-cyclodextrin; (f) fluorinated-cyclodextin (βC6F13: R=C6F13); and (g) octadecylperylene-cyclodextrin. The chemical structures in (b), (d), (e), and (f) depict the compounds studied in refs. [12,23,41,42] respectively. (a) Reprinted with permission from [39]. Copyright (2000) American Chemical Society. (c) reprinted with permission from [54]. Copyright (2013) American Chemical Society. (g) reprinted with permission from [38]. Copyright (2010) American Chemical Society. Methylation of the secondary cyclodextin faces in (a), (e), (f), (g) yields permethylated derivatives.