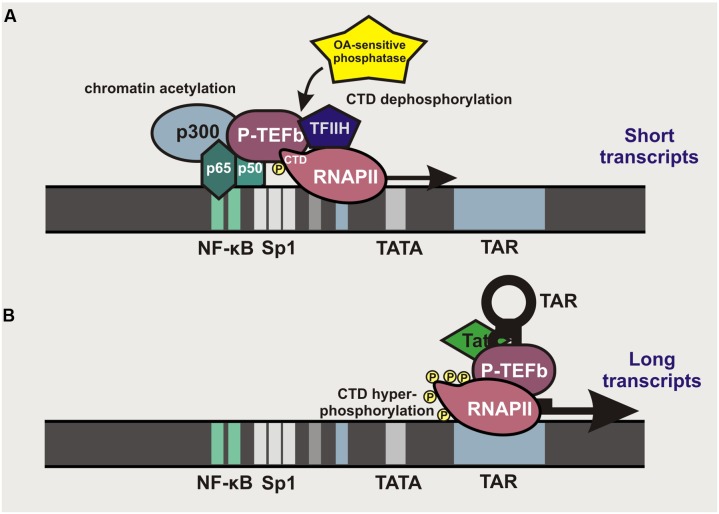
FIGURE 2.
Role of κB binding sites in primate lentiviral LTR-mediated transcription. (A) Localization of κB binding sites in primate lentiviral LTRs. NF-κB binding allows recruitment of p300 to initiate chromatin acetylation and to render the LTR better accessible for RNAPII. NF-κB also recruits P-TEFb, which binds to the CTD of RNAPII and strongly enhances its processivity. De-phosphorylation of the CTD by an OA-sensitive phosphatase terminates the elongation, resulting in the production of short TAR-containing transcripts. (B) In the presence of the viral Tat protein, transcription of proviral DNA is maintained independently of NF-κB. Tat binds to the short hairpin loop of TAR and recruits P-TEFb to the RNAPII, thereby allowing efficient elongation and generation of full-length viral transcripts.