Table 2. Hemispheric differences in the PCS morphology in males and females.
| Dataset 1 (right handed) |
Dataset 2 (right handed) |
Dataset 3 (right handed) |
Dataset 4 (left handed) |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prominent | Present | Absent | Prominent | Present | Absent | Prominent | Present | Absent | Prominent | Present | Absent | ||||
| Male | |||||||||||||||
| Total | 169(100) | 157(100) | 60(100) | 10(100) | |||||||||||
| Left | 40(24) | 70(41) | 59(35) | 15(10) | 40(25) | 102(65) | 7(12) | 13(22) | 40(66) | 1(10) | 4(40) | 5(50) | |||
| Right | 14(8) | 34(20) | 121(72) | 0(0) | 21(13) | 135(87) | 1(1) | 4(7) | 55(92) | 0(0) | 1(10) | 9(90) | |||
| Analysis | 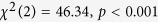 |
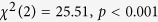 |
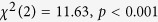 |
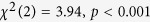 |
|||||||||||
| Female | |||||||||||||||
| Total | 163(100) | 169(100) | 68(100) | 31(100) | |||||||||||
| Left | 14(9) | 70(43) | 79(48) | 14(8) | 42(25) | 113(67) | 6(9) | 24(35) | 38(56) | 5(16) | 7(23) | 19(61) | |||
| Right | 6(4) | 30(18) | 127(78) | 2(1) | 19(11) | 148(88) | 1(2) | 5(7) | 62(91) | 0(0) | 1(3) | 30(97) | |||
| Analysis | 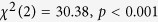 |
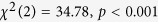 |
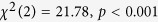 |
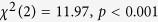 |
|||||||||||
The number of subjects with different PCS morphologies in the left or right hemisphere in males and females in each dataset. Percentages (%) are given in parentheses. Data, in the upper panel of the table, are the numbers of subjects with differences in the PCS morphology between the left and right hemispheres in males. Data in the lower panel of the table are the numbers of subjects with differences in the PCS morphology between the left and right hemispheres in females. ‘Total’ means the sum of the male and female participants in each dataset; ‘left’ and ‘right’ mean the left and right hemispheres, respectively. Analysis: the results of statistical tests.
