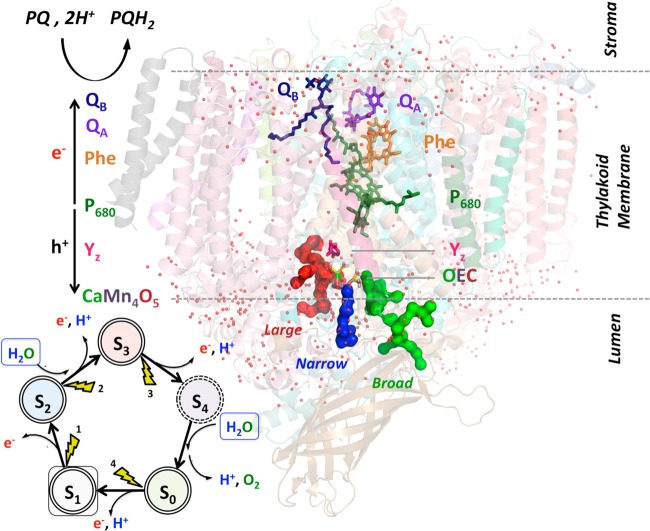
Figure 1.
Catalytic cycle of water oxidation, driven by solar light absorption. Each cycle is initiated by light absorption by the chlorophylls P680, followed by a charge separation. On the donor side, the electron sequentially reduces the special pheophytin and the pair of quinones QA and QB. After accepting two electrons, QBH2 is replaced by an oxidized quinone from a plastoquinone (PQ) pool. On the donor side, the hole oxidizes tyrosine Yz, which in turn oxidizes the oxygen-evolving complex. In each turn of the cycle, the OEC of PSII evolves through “storage” states, Sn (n = 0–4), catalyzing water splitting, as follows: 2H2O → O2 + 4H+ + 4e–. The water supply and proton release are likely happening through the water channels (labeled Large, Narrow and Broad) surrounding the OEC on the luminal side.