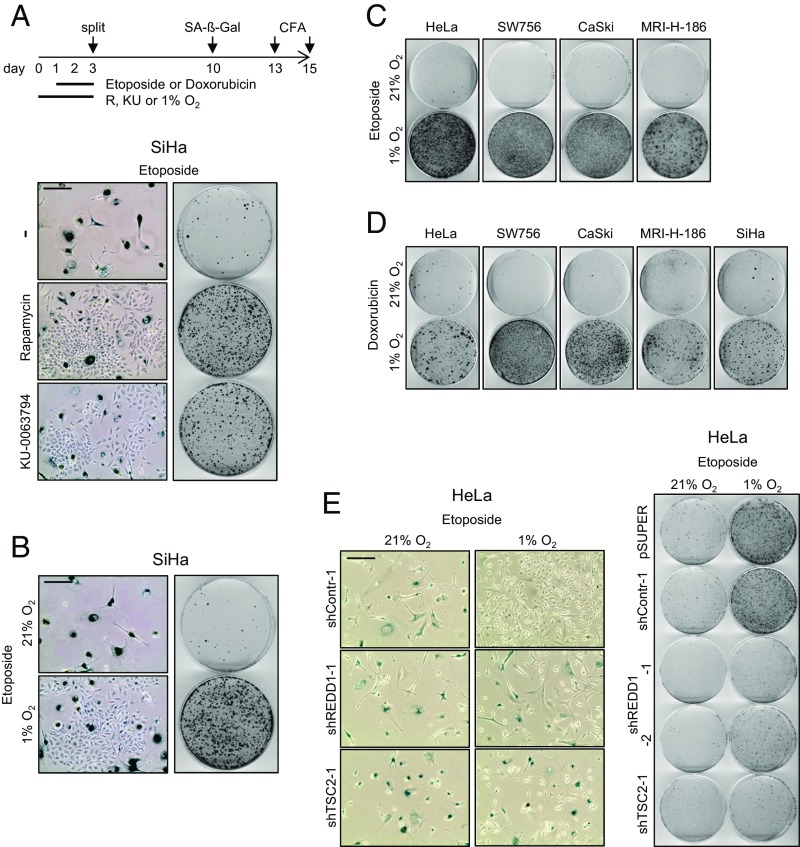
Fig. 4.
CT-induced senescence in HPV-positive cancer cells depends on mTOR signaling and is counteracted by hypoxia. (A) SiHa cells were treated under normoxia with etoposide, in either the absence (−) or the presence of rapamycin or KU-0063794. (Left) Senescence assays (SA-β-Gal staining). (Scale bar: 200 µm.) (Right) CFAs. Scheme above: Treatment protocol for Fig. 4 A–D, further detailed in the text. (B) SiHa cells were treated for 48 h with etoposide under normoxia or hypoxia, and subsequently cultured under normoxia. (Left) Senescence assays (SA-β-Gal staining). (Scale bar: 200 µm.) (Right) CFAs. (C and D) Normoxic and hypoxic HPV16- and HPV18-positive cancer cell lines were exposed to etoposide (C) or doxorubicin (D) at 21% or 1% O2, and subsequently analyzed by CFAs under normoxia. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with shRNA expression vectors for shREDD1-1, shREDD1-2, or shTSC2-1 and cultured under normoxia or hypoxia. (Left) Senescence assays (SA-β-Gal staining) of cells subsequently cultured under normoxia. (Scale bar: 200 µm.) (Right) Corresponding CFAs. Control cells were transfected with empty vector (pSUPER) or with a vector expressing shContr-1. Treatment protocol corresponds to the scheme indicated in Fig. 3E, but with additional etoposide treatment at days 2–4.