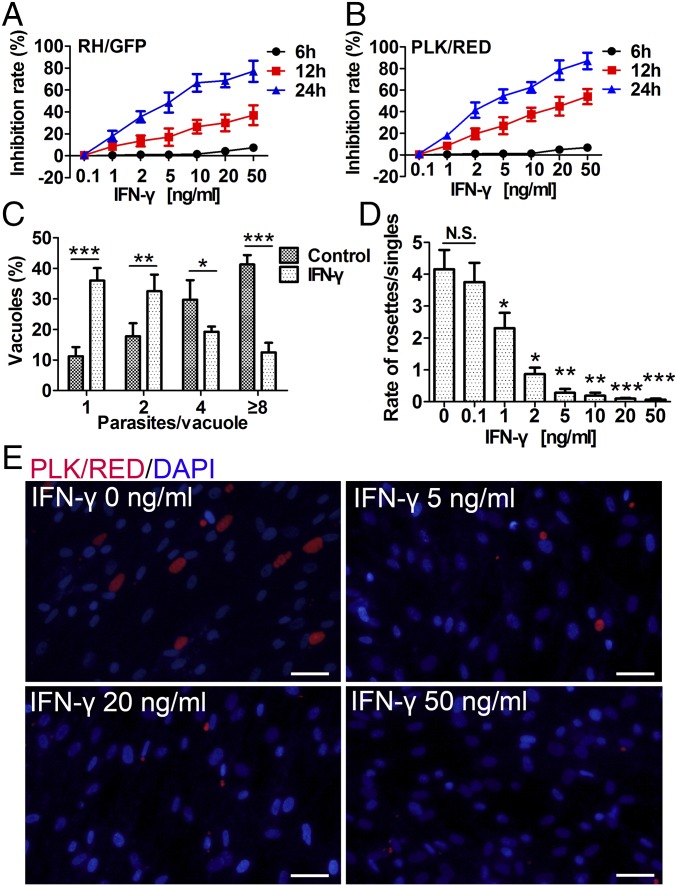
Fig. 1.
IFN-γ–stimulated human MSCs dose-dependently inhibit the growth of T. gondii. Human MSCs were pretreated for 48 h with IFN-γ and then infected with T. gondii (RH/GFP or PLK/RED). (A and B) T. gondii growth inhibition rates were calculated at 6, 12, and 24 h postinfection (A, RH/GFP; B, PLK/RED). (C) At 24 h postinfection, the number of parasites per vacuole in IFN-γ–stimulated (20 ng/mL) hMSCs and unstimulated hMSCs (controls) were calculated (PLK/RED). (D) At 48 h postinfection, ratios of intracellular T. gondii rosettes and PVs containing a single parasite were presented (PLK/RED). (E) Representative fluorescence images of D. DNA was stained with DAPI. (Scale bars: 20 μm.) All presented values are means ± SD, n = 4. Statistical significance was indicated by comparison with controls. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001; N.S., not significant.