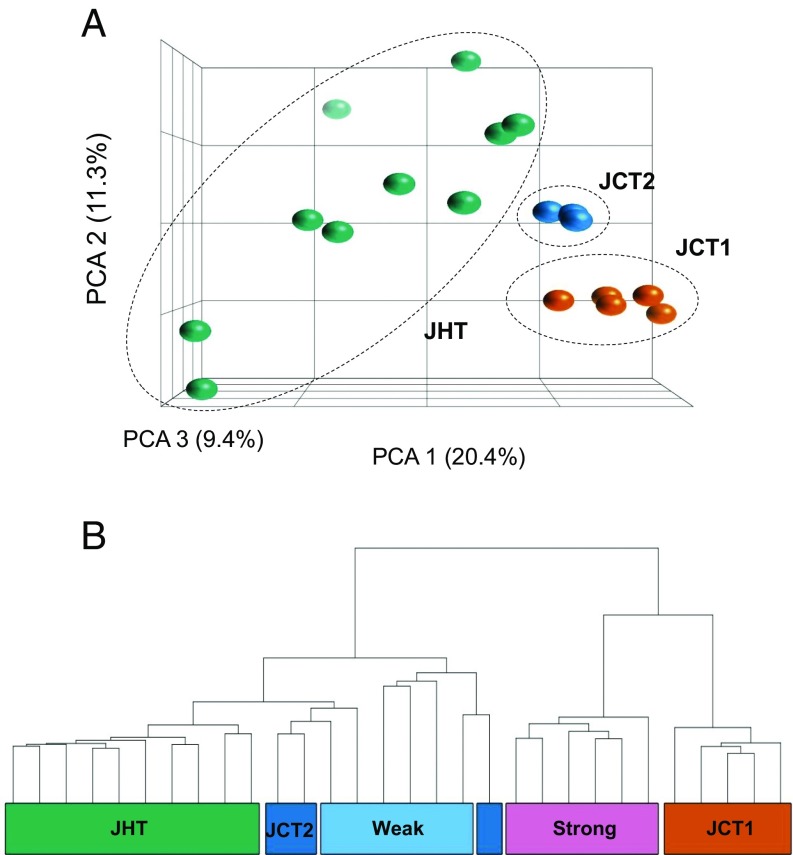
Fig. 4.
Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of juveniles (control, JCT; heat-treated, JHT) analyzed at 37 dpf shows groups related to sex (JCT, n = 8; JHT, n = 10). (A) PCA plot produced by expression profiles showing JCT clustered into two groups, namely JCT1 (orange) with five individuals and JCT2 (dark blue) with three individuals. All 10 JHT individuals (green) were placed in a single group. (B) Hierarchical clustering of control and heat-exposed juveniles together with Tg(vasa:vasa-egfp) juveniles using the 425 differentially expressed transcripts between JCT1 (orange) and JCT2 (dark blue). Juveniles in the JCT1 group were most likely females, as they clustered with transgenic juveniles that showed strong fluorescence intensity (future females; pink). The JCT2 juveniles were most likely males, as they were in the same node as the transgenic juveniles with weak fluorescence intensity (future males; light blue). All of the 10 heat-treated juveniles (JHT; green) clustered with the weak fluorescence transgenic juveniles and JCT2, indicating a similar male-like transcriptomic profile regardless of their genetic sex.