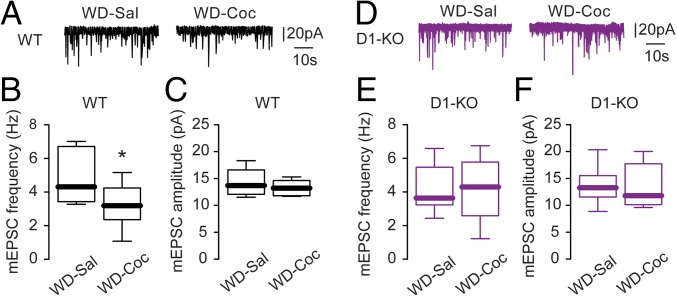
Fig. 6.
Effect of acute cocaine challenge after withdrawal on AMPA glutamate receptor-mediated synaptic currents in D1-MSNs in the NAc core. After 14 d of withdrawal (WD) from chronic exposure to cocaine (i.p., 15 mg/kg), WT (A–C) and WAVE1 D1-KO mice (D–F) were acutely challenged with saline or cocaine (5 mg/kg). Sample traces of mEPSC from WT (A) or D1-KO (D) D1-MSNs in the NAc core are shown with vertical and horizontal scale bars. mEPSC frequency (B) was reduced by an acute cocaine challenge without altering mEPSC amplitude (C) in WT mice (Sal challenge: n = 9 cells, 6 mice; Coc challenge: n = 6 cells, 3 mice). mEPSC frequency (E) and amplitude (F) were unchanged by an acute cocaine challenge after withdrawal in D1-KO mice (Sal challenge: n = 10 cells, 7 mice; Coc challenge: n = 8 cells, 6 mice). Data were analyzed by Mann–Whitney nonparametric analysis (*P < 0.05) and presented as box-and-whisker plots indicating the median, quartiles, and range.