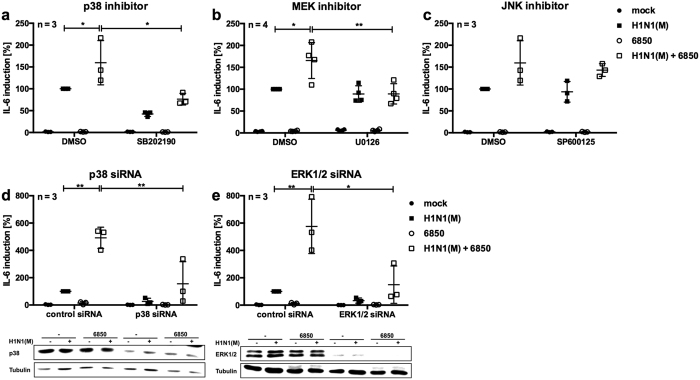
Figure 6. Specific inhibition of the MAPK p38 or the Raf/MEK/ERK signalling pathway reduces IL-6 mRNA levels during super-infection.
A549 cells were treated with 10 μM p38 inhibitor (SB202190) (a), 10 μM MEK inhibitor (U0126) (b), 10 μM JNK inhibitor (SP600125) (c) or DMSO as solvent control for 0.5 h. A549 cells were transfected with 33 nM siRNA directed against p38 (d), ERK1/2 (e) or control siRNA and incubated for 48 h. Subsequently, cells were infected with IV H1N1(M) (MOI 5) for 0.5 h and super-infected with S. aureus 6850 (MOI 50) (a–e), in the presence of the inhibitors (a–c). Extracellular bacteria were removed by gentamicin treatment 3 h after bacterial infection (a–e), and supplemented with the specific inhibitors (a–c). Expression of p38 (d) and ERK1/2 (e) was monitored by Western blot analysis (original blots are depicted in Supplementary Fig. S8d). IL-6 mRNA levels were measured in duplicates at 8 h p.i. Means ± SD of at least three independent experiments are shown. IV-infected samples of control cells were arbitrarily set as 100%. After normalisation, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests were performed for comparison of IV H1N1(M)-infected and IV H1N1(M)/S. aureus 6850 super-infected samples, control and treated IV-infected samples, and control and treated super-infected samples (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).