Abstract
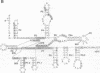
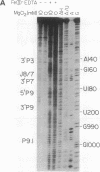
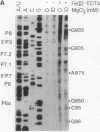
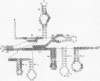
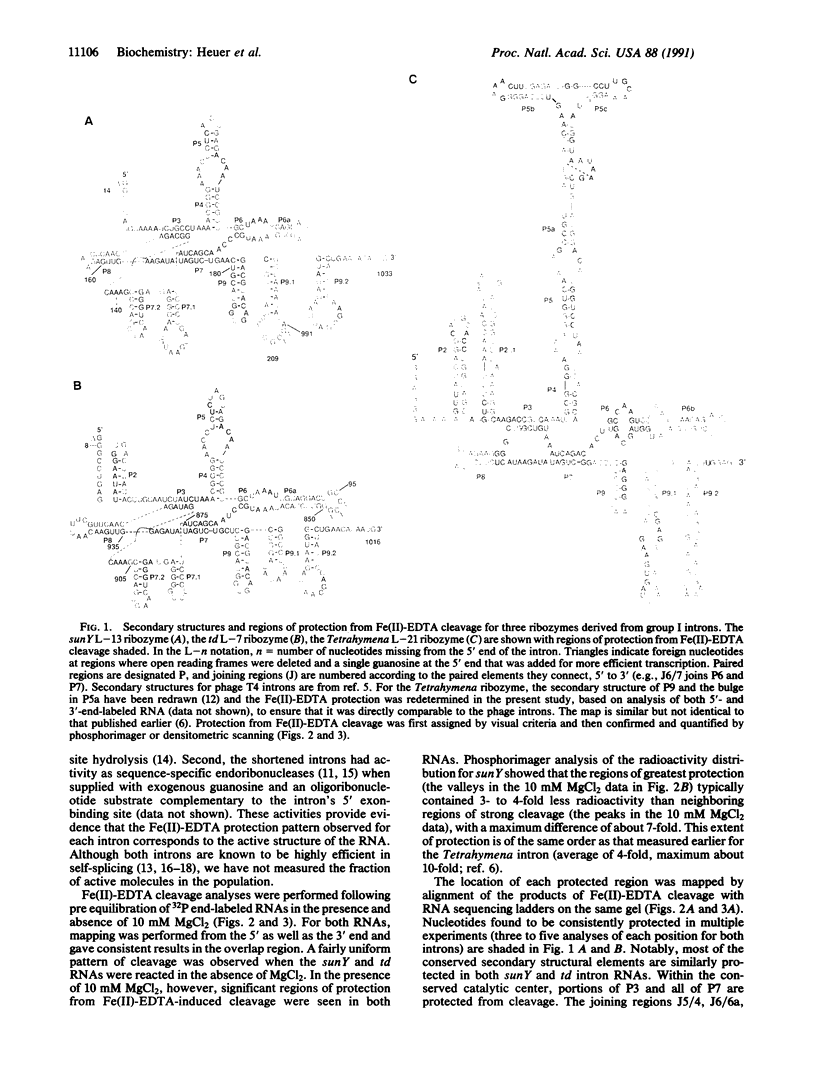
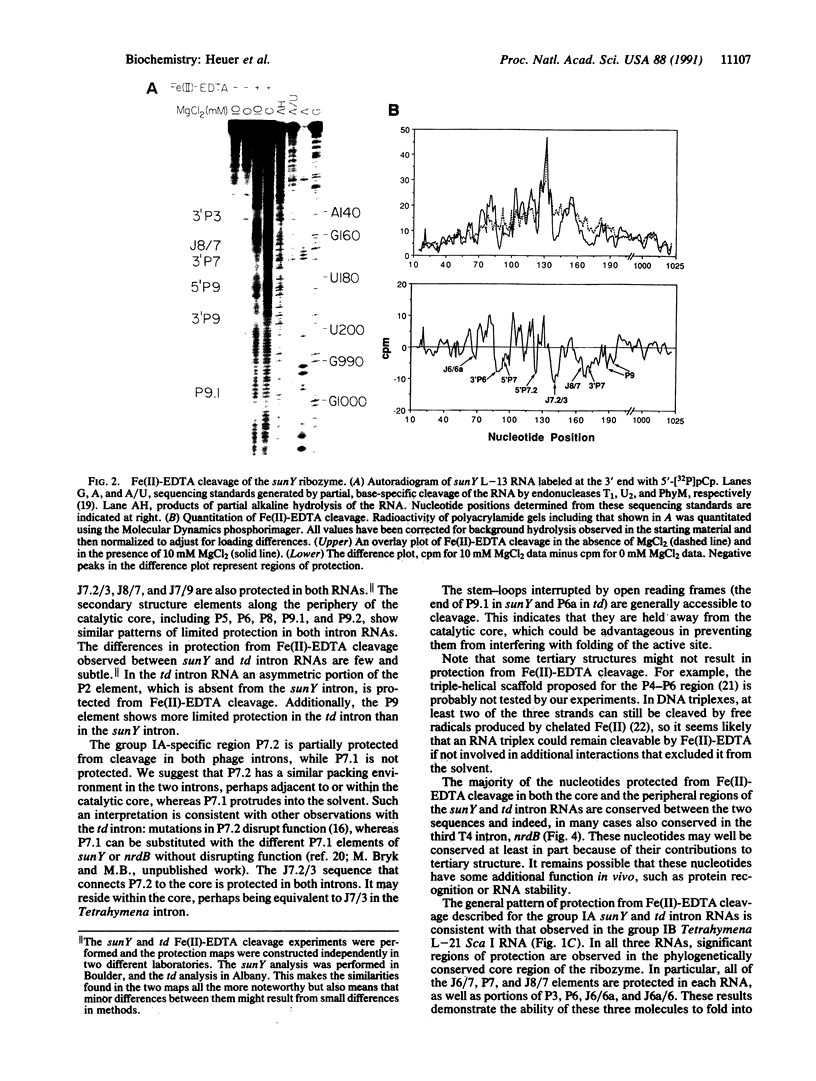
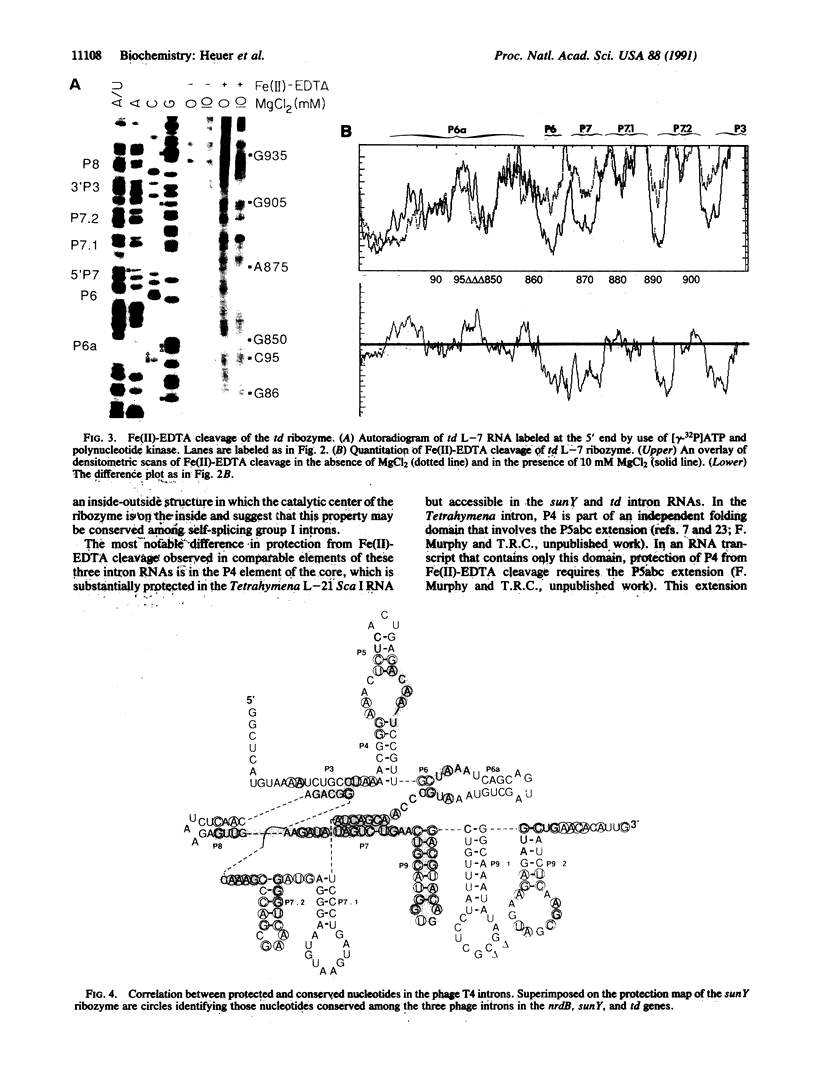
Fe(II)-EDTA, a solvent-based cleavage reagent that distinguishes between the inside and outside surfaces of a folded RNA molecule, has revealed some of the higher-order folding of the group IB intron from Tetrahymena thermophila pre-rRNA. This reagent has now been used to analyze the bacteriophage T4 sunY and td introns, both of which are members of the group IA subclass. Significant portions of the phylogenetically conserved secondary structure are protected from Fe(II)-EDTA cleavage. However, the P4 secondary structure element, which is substantially protected in the Tetrahymena intron, is available for cleavage in the two T4 introns. We conclude that a family of catalytic RNAs (ribozymes) that possess similar secondary structures and have similar activities fold into similar but nonidentical tertiary structures that nevertheless serve to internalize portions of the catalytic center. Furthermore, comparison of cleavage patterns of the sunY and td intron RNAs indicates that conserved nucleotides outside as well as within the catalytic core participate in the tertiary structure.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M., Chandry P. S., Pedersen-Lane J. Genetic delineation of functional components of the group I intron in the phage T4 td gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:181–192. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. Phage T4 introns: self-splicing and mobility. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:363–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryk M., Belfort M. Spontaneous shuffling of domains between introns of phage T4. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):394–396. doi: 10.1038/346394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D. W., Cech T. R. Iron(II)-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid catalyzed cleavage of RNA and DNA oligonucleotides: similar reactivity toward single- and double-stranded forms. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1355–1361. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D. W., Cech T. R. Visualizing the higher order folding of a catalytic RNA molecule. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):401–407. doi: 10.1126/science.1989074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor P. J., Flanegan J. B., Cech T. R. A conserved base pair within helix P4 of the Tetrahymena ribozyme helps to form the tertiary structure required for self-splicing. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3391–3399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway Salvo J. L., Coetzee T., Belfort M. Deletion-tolerance and trans-splicing of the bacteriophage T4 td intron. Analysis of the P6-L6a region. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 5;211(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90264-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicke B. J., Christian E. L., Yarus M. Stereoselective arginine binding is a phylogenetically conserved property of group I self-splicing RNAs. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3843–3851. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. New reactions of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena and the mechanism of self-splicing. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. F., van der Horst G., Inoue T. Catalytic activity is retained in the Tetrahymena group I intron despite removal of the large extension of element P5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7879–7889. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham J. A., Cech T. R. Defining the inside and outside of a catalytic RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):276–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2501870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Ellington A. D., Couture S., Szostak J. W. Phylogenetic and genetic evidence for base-triples in the catalytic domain of group I introns. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):578–580. doi: 10.1038/347578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Gott J. M., Xu M. Q., Lang B. F., Michel F., Tomaschewski J., Pedersen-Lane J., Belfort M. Structural conservation among three homologous introns of bacteriophage T4 and the group I introns of eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1151–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Iron(II) EDTA used to measure the helical twist along any DNA molecule. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):679–681. doi: 10.1126/science.2996145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Q., Shub D. A. The catalytic core of the sunY intron of bacteriophage T4. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Been M. D., Cech T. R. The Tetrahymena ribozyme acts like an RNA restriction endonuclease. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):429–433. doi: 10.1038/324429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Grosshans C. A., Cech T. R. Sequence-specific endoribonuclease activity of the Tetrahymena ribozyme: enhanced cleavage of certain oligonucleotide substrates that form mismatched ribozyme-substrate complexes. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8924–8931. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Horst G., Christian A., Inoue T. Reconstitution of a group I intron self-splicing reaction with an activator RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]