Figure 1. Intraluminal tranexamic acid reduces gut injury and inflammation following hemorrhagic shock.
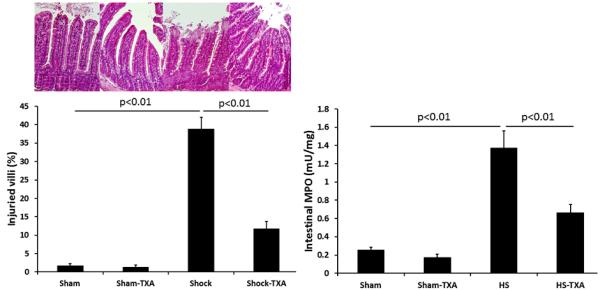
C57BL/6J mice underwent 90 minutes of hemorrhagic shock followed by the intraluminal injection of tranexamic acid into the small intestine. Three hours later, small intestine was analyzed for histopathologic injury expressed as the % of injured villi with representative images shown. Inflammation was assessed by measuring myeloperoxidase activity. Results are expressed as mean ± SE; n=8/group. Abbreviations: HS= hemorrhagic shock; TXA-tranexamic acid
