Figure 2. Intraluminal tranexamic acid reduces pulmonary injury and inflammation following hemorrhagic shock.
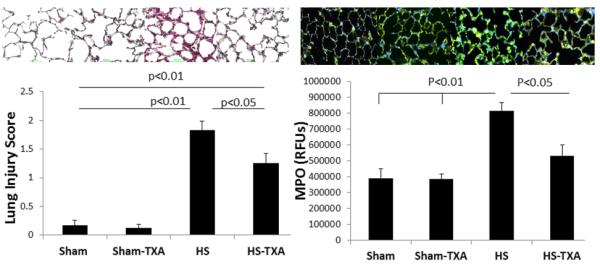
C57BL/6J mice underwent 90 minutes of hemorrhagic shock followed by the intraluminal injection of tranexamic acid into the small intestine. Three hours later, lungs were analyzed for histopathologic injury using a three point scoring system; representative photomicrographs are shown. Myeloperoxidase immunofluorescence staining was used to assess lung inflammation; representative images shown along with the corresponding images. Results are expressed as mean SE; n=8/group. Abbreviations: HS= hemorrhagic shock; TXA- tranexamic acid; MPO=myeloperoxidase; RFU= relative fluorescent units
