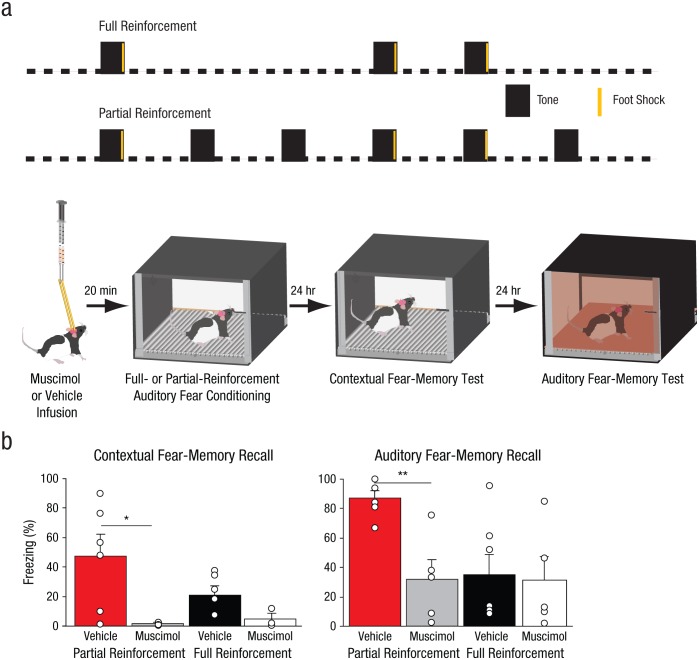
Fig. 5.
Method and results from Experiment 4. Four groups of rats (n = 5–7 per group) received intrahippocampal infusions of muscimol or vehicle before auditory fear conditioning (10-s tone, 2-s foot shock; 70-s intertrial interval), as illustrated in (a). Conditioning was either partially reinforced (50% chance of a foot shock following a tone) or fully reinforced (100% chance of a foot shock following a tone). The next day, all the rats were returned to the conditioning context for 10 min. The day after that, all rats received 14 tone presentations, and auditory fear recall was measured as average freezing across the first two tone presentations for each group. The bar graphs in (b) show the mean percentage of time the rats displayed freezing behavior in each reinforcement-schedule group, separately for contextual fear-memory recall and auditory memory-fear recall. The small open circles represent the percentage of time that individual rats displayed freezing behavior. Error bars represent +1 SEM. Asterisks represent significant differences between groups (*p < .05, **p < .01).