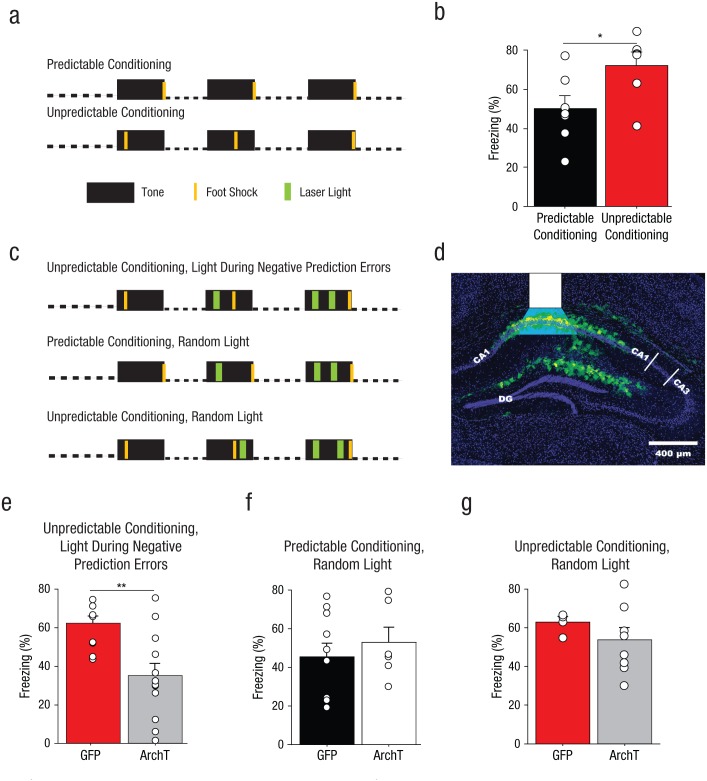
Fig. 6.
Method and results for Experiment 5. Mice without implants (n = 6–7 per group) were fear conditioned with three pairings of a 30-s tone with a 2-s foot shock delivered with predictable or unpredictable timing, as illustrated in (a). Auditory fear recall was then tested in a novel context. The graph in (b) shows mean percentage of time the mice without implants displayed freezing behavior, separately for predictable- and unpredictable-conditioning groups. The small open circles represent the percentage of time that individual mice displayed freezing behavior. The mice in the ArchT groups received a bilateral infusion of an adenoassociated virus (AAV) expressing the silencing opsin ArchT fused to green fluorescent protein (GFP); the mice in the GFP groups received an AAV expressing GFP. Both viruses targeted cornu ammonis (CA) 1 of dorsal hippocampus. The mice that received brain implants were fear conditioned with three pairings of a 30-s tone with a 2-s foot shock, delivered along with 4-s applications of green laser light, under one of three conditions, as illustrated in (c). Mice in the unpredictable-conditioning/light-during-negative-prediction-error group (n = 10–12) received intrahippocampal delivery of green light (λ = 575 nm) during 4-s periods (the 2 s in which foot shock was actually delivered, and an additional second of light delivery before and after the time of the previous foot shock) surrounding the times at which foot shock had been administered on previous trials. Thus, on Trial 2, light was applied during the time at which the foot shock had occurred on Trial 1. On Trial 3, light was applied during the times at which foot shock had occurred on Trials 1 and 2. Mice in the predictable-conditioning/random-light group received intrahippocampal green light at the same times (relative to conditioned stimulus, or CS, onset) as mice in the unpredictable-conditioning/light-during-negative-prediction-error group, but foot shock had never occurred at these times for the predictable-conditioning/random-light groups. Mice in the predictable-conditioning/random-light group (n = 5–8) received intrahippocampal green light during 4-s periods in which foot shock had never been delivered. Expression of GFP after infection with ArchT is shown for a representative brain section in (d). The white overlay indicates the location of the fiber-optic tip and the estimated light spread. DG = dentate gyrus. Auditory fear-memory recall was measured across two tone presentations during a subsequent laser-free extinction session. The bar graphs show mean percentage of time that the mice displayed freezing behavior as a function of infusion type for (e) the unpredictable-conditioning/light-during-negative-prediction-error group, (f) the predictable-conditioning/random-light group, and (g) the unpredictable-conditioning/random-light group. The small open circles represent the percentage of time that individual mice displayed freezing behavior. Error bars indicate +1 SEM. Asterisks represent significant differences between infusion conditions (*p < .05, **p < .01).