Figure 9. Multi-pronged targeting of the AR and PI3K/mTORC1 axis by salinomycin – a schematic illustration.
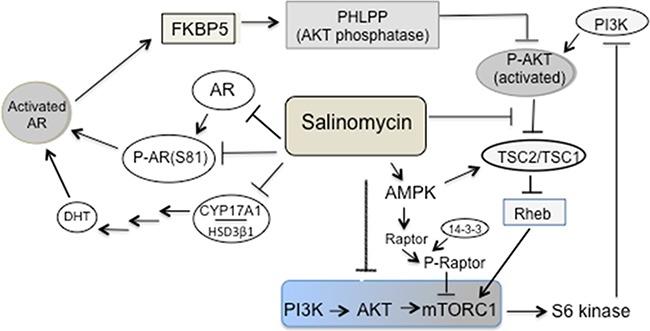
Reduction of AR expression, AR Ser-81 phosphorylation as well as CYP17A1 and HSD3β1 expression led to the inhibition of AR activity. Salinomycin inhibited the PI3K→AKT→mTORC1 axis due to 1) activation of AMPK, which in turn induced raptor phosphorylation and binding of 14-3-3 to phospo-raptor would dampen mTOR kinase function (14). Activated AMPK also augmented TSC2/TSC1 activity by mediating stimulatory phosphorylation of TSC2 at Ser-1387; 2) inhibition of the AKT→TSC2 axis, since inhibitory phosphorylation of TSC2 at Ser-939/Thr-1482, catalyzed by AKT, was reduced. Elevated TSC2/TSC1 activity led to mTORC1 inactivation. Salinomycin-mediated targeting of the AKT→TSC2 axis mitigated the impact of AKT activation caused by enhanced PI3K activity, which resulted from the loss of feedback repression.
