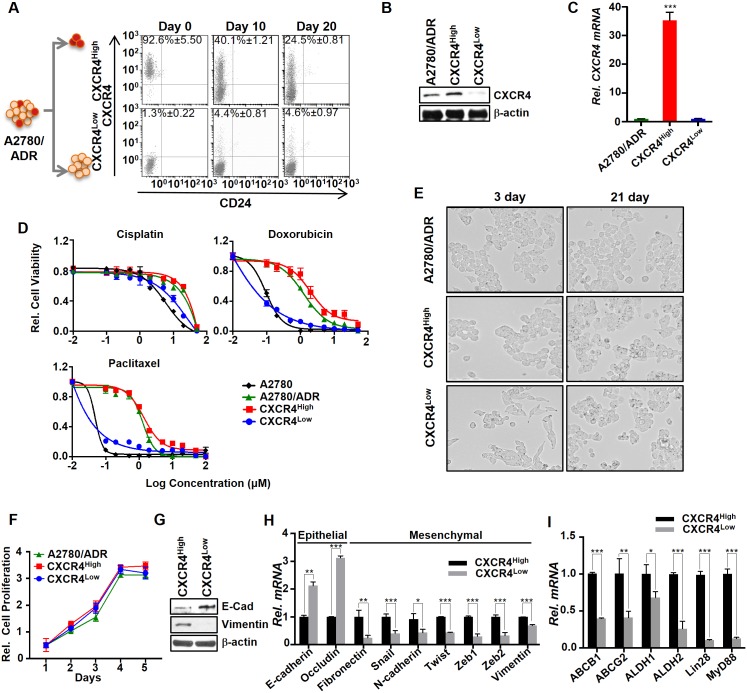
Fig 2. CXCR4High displayed drug-resistant and mesenchymal properties.
(A) FACS analysis showed that the freshly isolated CXCR4High and CXCR4Low eventually lost their purity over time. The cells were isolated by flow cytometry using APC-labeled CXCR4 antibody. (B and C) The CXCR4 expressions in A2780/ADR, CXCR4High, and CXCR4Low were determined using western blot and real-time PCR analysis. Results of western blot and real-time PCR were normalized to β-actin expression and the CXCR4 mRNA expression of CXCR4 in A2780/ADR cells were set to 1. (D) Plots of relative cell viability versus different drug treatments reveal that CXCR4High cells were intrinsically drug-resistant. The cell viability was determined by MTS assay. (E) Microscopic images (10x magnification) of CXCR4High and CXCR4Low. The two freshly isolated cell lineages from A2780/ADR display significantly different morphologies. After continuous culturing for 21 days, their morphology became similar, presumably because OVC prefers to maintain an equilibrium state between the two cell populations. (F) Comparison of the cell proliferation among A2780/ADR and its isolated CXCR4High and CXCR4Low lineages. CXCR4High exhibits the similar cell proliferation rate. (G and H) CXCR4High displayed mesenchymal phenotypes, as shown by the higher and lower expressions of the epithelial and mesenchymal markers, respectively, compared to CXCR4Low using western blot and real-time PCR. (I) CXCR4High also displayed higher expressions of cancer stem cell markers. Results of real-time PCR was normalized to β-actin expression and the mRNA gene expression of epithelial, mesenchymal and stem cell markers in CXCR4 High cells were set to 1. All our data represent means ± SD of three independent experiments (t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001).