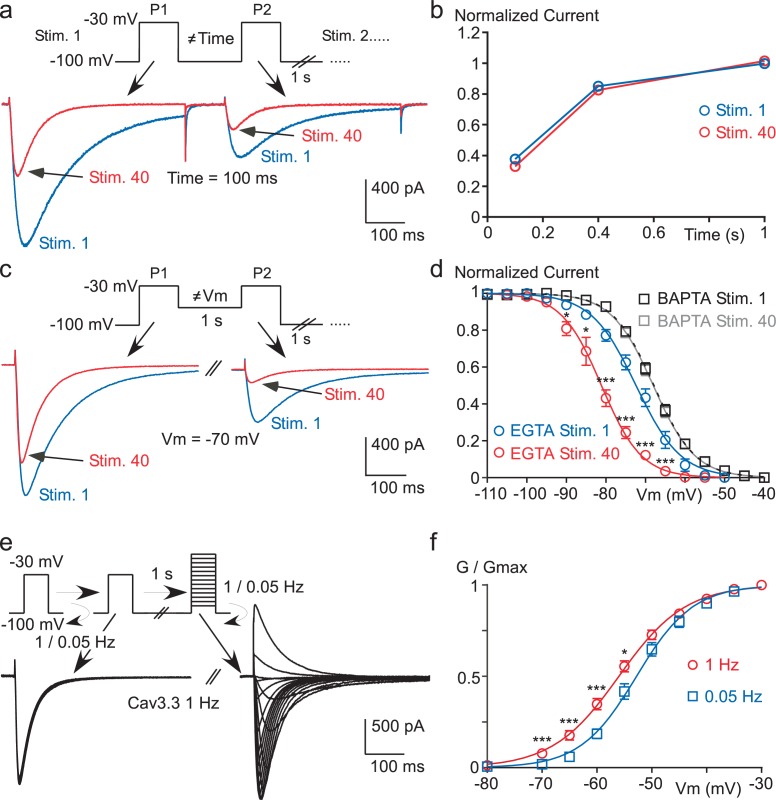
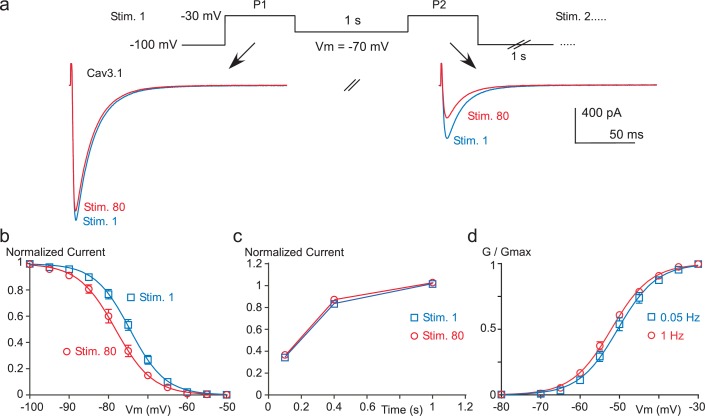
Figure 3. High frequency stimulation induces a Ca2+-dependent negative shift in the Cav3.3 steady-state inactivation properties.
(a–b) Recovery from short-term inactivation of the Cav3.3 current measured by a paired-pulse stimulation (inter-stimulation 1 s) applied 40 times (Stim. 1 to Stim. 40). The interval between the first pulse (P1) and the second pulse (P2), i.e. interpulse, is 100, 400 or 1000 ms, as presented in (a) for an interpulse interval of 100 ms. The recovery from short-term inactivation (P2/P1), as a function of the interpulse duration is quantified for the first stimulation (Stim. 1) and the 40th stimulation (Stim. 40) (b, n = 5–7 per point). (c–d) Steady-state inactivation of the Cav3.3 current measured using a paired-pulse stimulation applied 40 times. The Vm between the two pulses ranged from −110 to −40 mV, as illustrated in (c) for a Vm of −70 mV. Steady-state inactivation (measured at P2) as a function of the Vm is determined for the first stimulation (Stim. 1) and for the 40th stimulation (Stim. 40) (d, n = 5–9 per point). (e–f) Current-voltage (I–V) protocol (e) and activation curve (f) of the Cav3.3 current during 1 Hz or 0.05 Hz stimulation. The Cav3.3 current was stimulated at 1 Hz or 0.05 Hz until reaching the steady-state just before I-V protocols, which were performed by a double-pulse protocol to maintain the 1 Hz stimulation effect (n = 17).