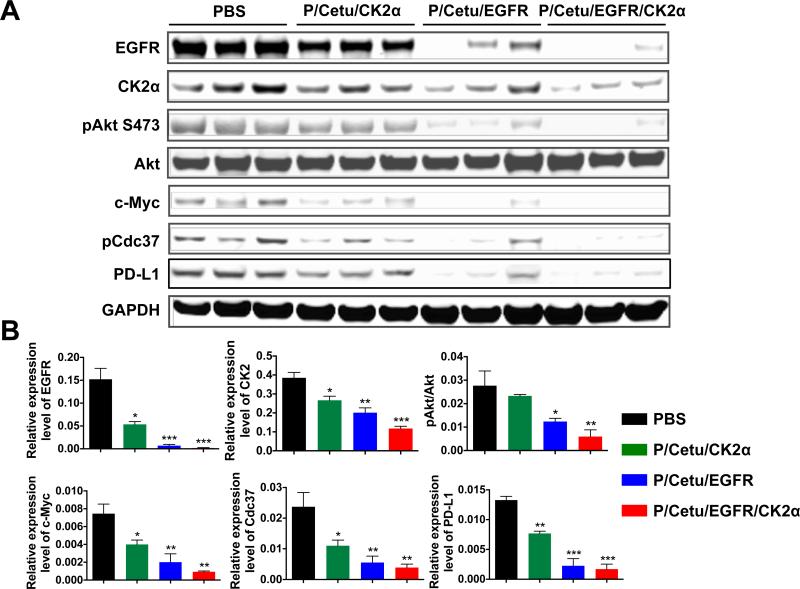
Figure 4.
Expression of molecular targets in xenogeneic LN229 brain tumors revealed by western blot. A) Protein expression of EGFR, CK2α, phosphorylated Akt [Ser473] (pAkt S473), total Akt, c-Myc, phosphorylated Cdc37 (pCdc37), and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). Treatment with all nanobioconjugates resulted in significantly lower expression of the analyzed proteins. Three independent tumor specimens per each treatment group were analyzed. AON - antisense oligonucleotide, PBS - phosphate-buffered saline, Cetu - cetuximab, CK2α - catalytic α subunit of protein kinase CK2, EGFR - epidermal growth factor receptor, P/Cetu/CK2α - nanobioconjugate with AON against CK2α, P/Cetu/EGFR - nanobioconjugate with AON against EGFR, P/Cetu/EGFR/CK2α - nanobioconjugate with AONs against both EGFR and CK2α, GAPDH - glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. B) Band intensities of tumor samples were quantified by Image Studio software and normalized against GAPDH or Akt (for pAkt) as a control. All proteins showed statistically significant decreases following the treatments. Note significantly reduced expression of EGFR upon anti-CK2α treatment and vice versa. The results represent means ± SEMs vs. PBS treatment. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.