Figure 1.
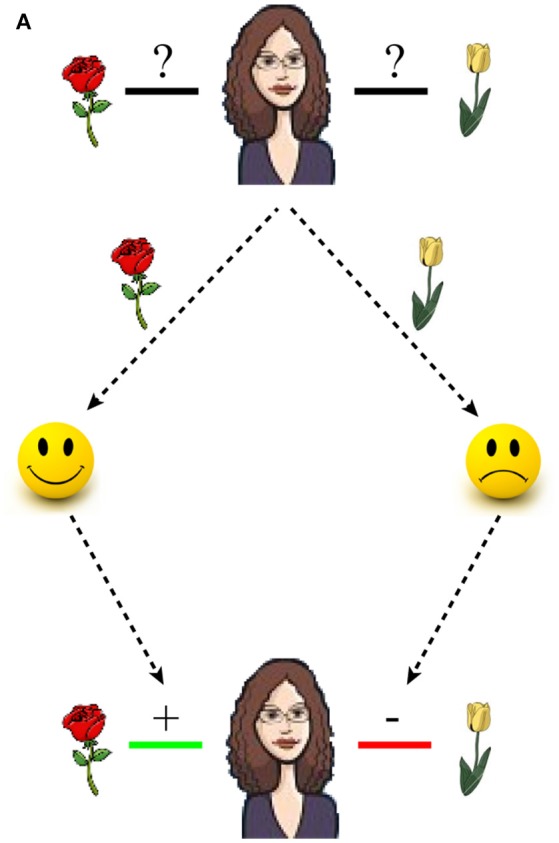
Shaping associative memory via positive and negative feedback. The problem of buying a spouse the right type of flowers becomes trivial by remembering the positive and negative associations between the spouse and each type of flower. In this example, a rose elicits a smile which causes a positive association while a tulip causes sadness, thus creating a negative association.
