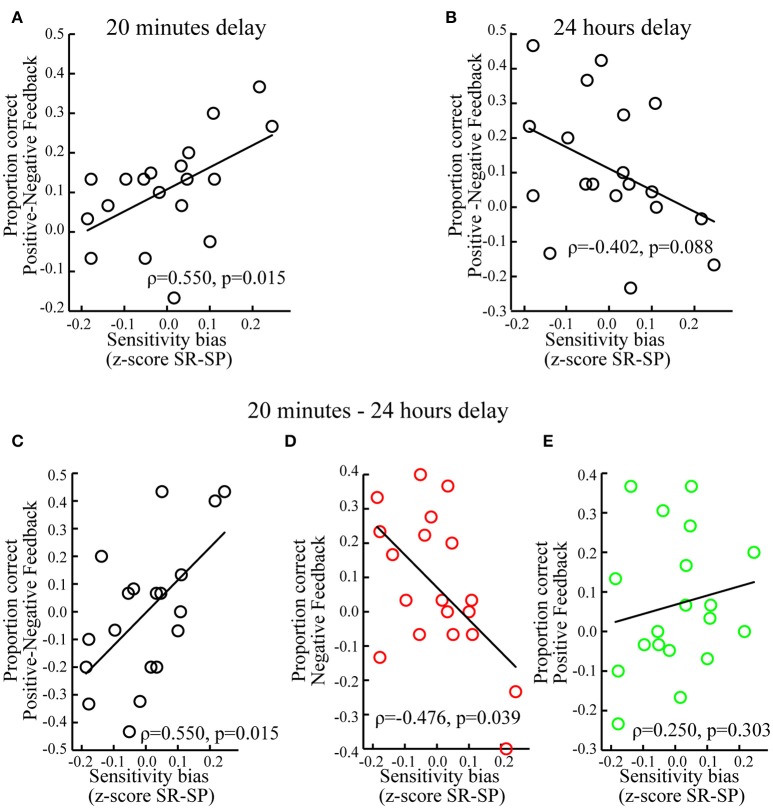
Figure 5.
Individual differences. (A) When tested after 20 min, memory performance for positive vs. negative feedback correlated positively with the sensitivity bias, i.e., z-scored Sensitivity to Reward (SR) minus z-scored Sensitivity to Punishment (SP). (B) When tested after 24 h, memory performance for positive vs. negative feedback correlated marginally and negatively with the sensitivity bias. (C) For positive vs. negative feedback, memory performance correlated positively with the sensitivity bias, when memory was tested after 20 min as compared to 24 h. (D) For negative feedback, memory performance correlated negatively with the sensitivity bias, when memory was tested after 20 min as compared to 24 h. (E) For positive feedback, memory performance did not correlate significantly with the sensitivity bias, when memory was tested after 20 min as compared to 24 h. For display purposes non-ranked data and linear regression slopes are shown.