Figure 2.
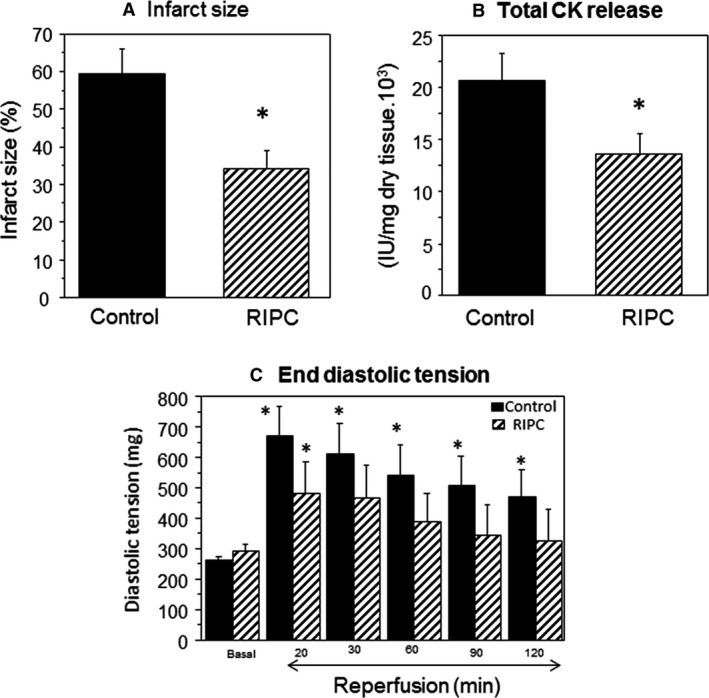
Cardiac ischemia and reperfusion injury in Langendorff heart. The Effects of RIPC on infarct size and creatine kinase release. Langendorff‐perfused hearts with or without RIPC application were exposed to 30 min ischemia followed by 120 min reperfusion. (A) Infarct size measured using TTC and expressed as percentage of risk area. Inset shows representative sections from control and RIPC hearts with darker parts indicating viable tissue. (B) Creatine kinase activity from hearts effluents collected preischemia and during reperfusion. (C) The effects of RIPC on diastolic tension measured at 20, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min during reperfusion. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6–10 hearts/group for different endpoints). *P < 0.05 versus corresponding control (or basal) using either unpaired t‐test (A and B) or repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni‐Dunn test (C). RIPC, remote ischemic preconditioning; TTC, triphenyltetrazolium chloride; ANOVA, analysis of variance.
