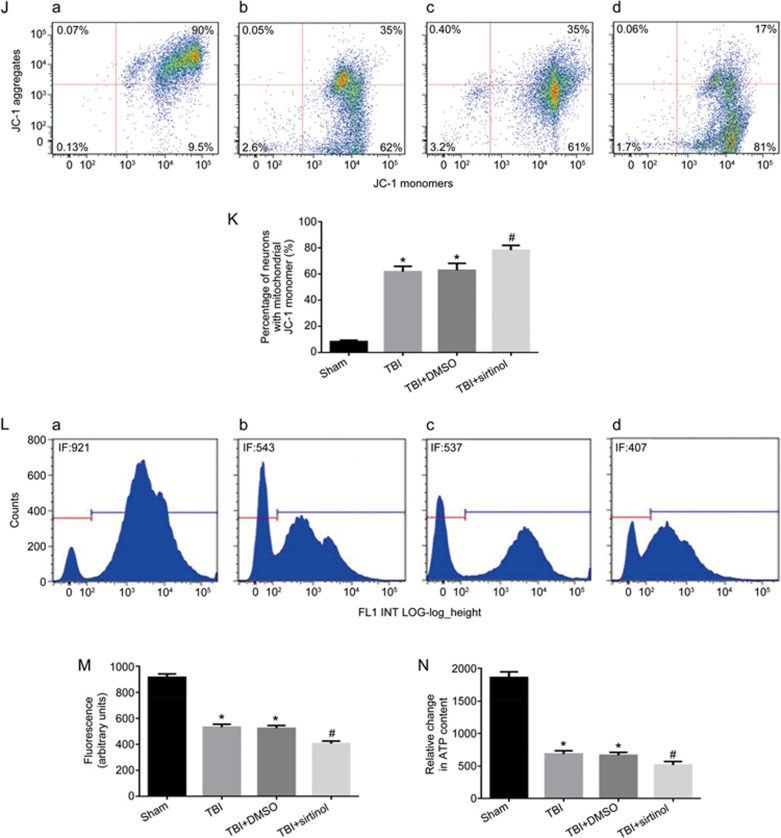
Figure 4J-4N.
SIRT1 inhibitor exacerbates TBI-induced mitochondrial damage, promotes neuronal apoptosis and activates p38 MAPK signaling. Rats were injected intraperitoneally with the SIRT1 inhibitor sirtinol (10 mg/kg) 30 min before LFP-induced TBI. After 12 h, rats were sacrificed. (J) The loss of ΔΨm was measured by JC-1 and analyzed by flow cytometry. (a–d) represent the sham group, TBI group, TBI+DMSO group and TBI+sirtinol group, respectively. (K) Quantification of mitochondrial depolarization expressed as JC-1 monomer (green fluorescence) in all treatment groups post-TBI. (L) mPTP opening was measured by staining with calcein-AM and CoCl2 and analyzed by flow cytometry for green fluorescence. (a–d) represent the sham group, TBI group, TBI+DMSO group and TBI+sirtinol group, respectively. (M) Quantification of mitochondrial green fluorescence intensity post-TBI in all treatment groups. (N) Quantification of the change in neuronal ATP levels following TBI in all treatment groups. SIRT1 inhibitor also increased the low ΔΨm (J, K) and the opening of mPTP (L, M), and decreased neuronal ATP levels (N). There was no difference between the TBI and the TBI+DMSO groups. n=6/group. Mean±SD. *P<0.05 vs sham group. #P<0.05 vsTBI group.