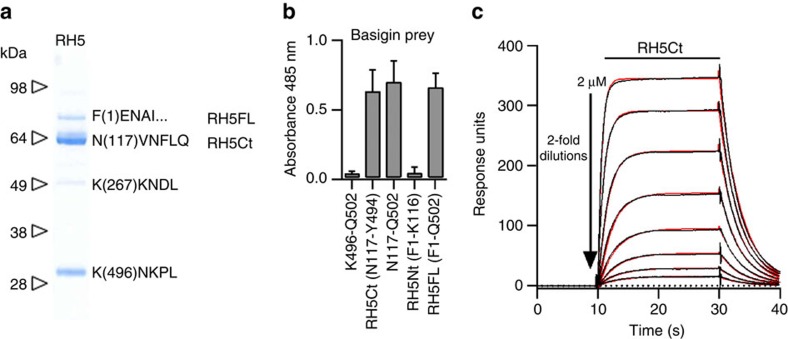
Figure 1. The N-terminal domain of RH5 is not involved in basigin binding.
(a) Purified tagged recombinant RH5 expressed by HEK293 cells resolved as four species by SDS–PAGE under reducing conditions. The N-terminal sequence of each species was determined by Edman degradation and is shown. (b) The N-terminal region of RH5 is not involved in basigin binding. The indicated RH5 fragments were expressed as biotinylated bait proteins and probed for interactions with a highly avid β-lactamase-tagged basigin prey protein using the AVEXIS assay. The full length (FL) and the major processed form (RH5Ct) of RH5 bound basigin but the N-terminal region (RH5Nt) did not. Bars represent means±95% confidence intervals; n=3. (c) Biophysical analysis of the RH5Ct-basigin interaction. Serial dilutions of the indicated concentrations of purified RH5Ct protein were injected over the biotinylated ectodomain of basigin immobilized on a streptavidin-coated sensor chip. The data showed excellent fits to a simple (1:1) binding model (red line). The binding parameters of RH5Ct did not differ significantly from those obtained from RH5FL (Supplementary Table 1) demonstrating that the N-terminal region of RH5 does not contribute to basigin binding affinity.